Solar Mounting Systems
Contact Us
- Building A06, Jimei Software Park, Xiamen, China
- +86-592-6683155
- [email protected]
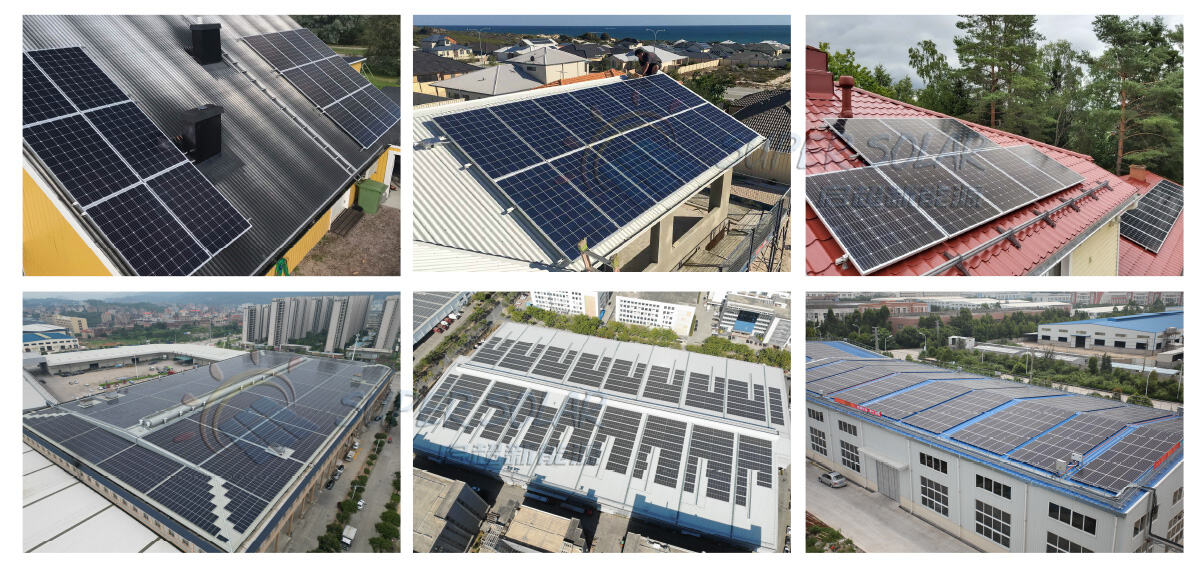
As metal roofs become increasingly popular in commercial and industrial (C&I) buildings, solar installers and project developers are looking for reliable, roof-safe photovoltaic (PV) mounting solutions specifically designed for metal roofing structures.
This guide explains how metal roof solar mounting systems work, the main roof types, and how to choose the right solution to ensure structural safety, long-term performance, and compliance with international standards.
Metal roofs are widely used in factories, warehouses, logistics centers, and commercial buildings because of their durability and load-bearing capacity. From a PV perspective, metal roofs offer several advantages:
· Long service life, often matching or exceeding PV system lifespan
· Strong structural capacity for distributed loads
· Large, unobstructed roof surfaces
· Compatibility with non-penetrating mounting systems
However, not all metal roofs are the same, and choosing the wrong mounting method can lead to leakage risks, structural issues, or warranty conflicts.

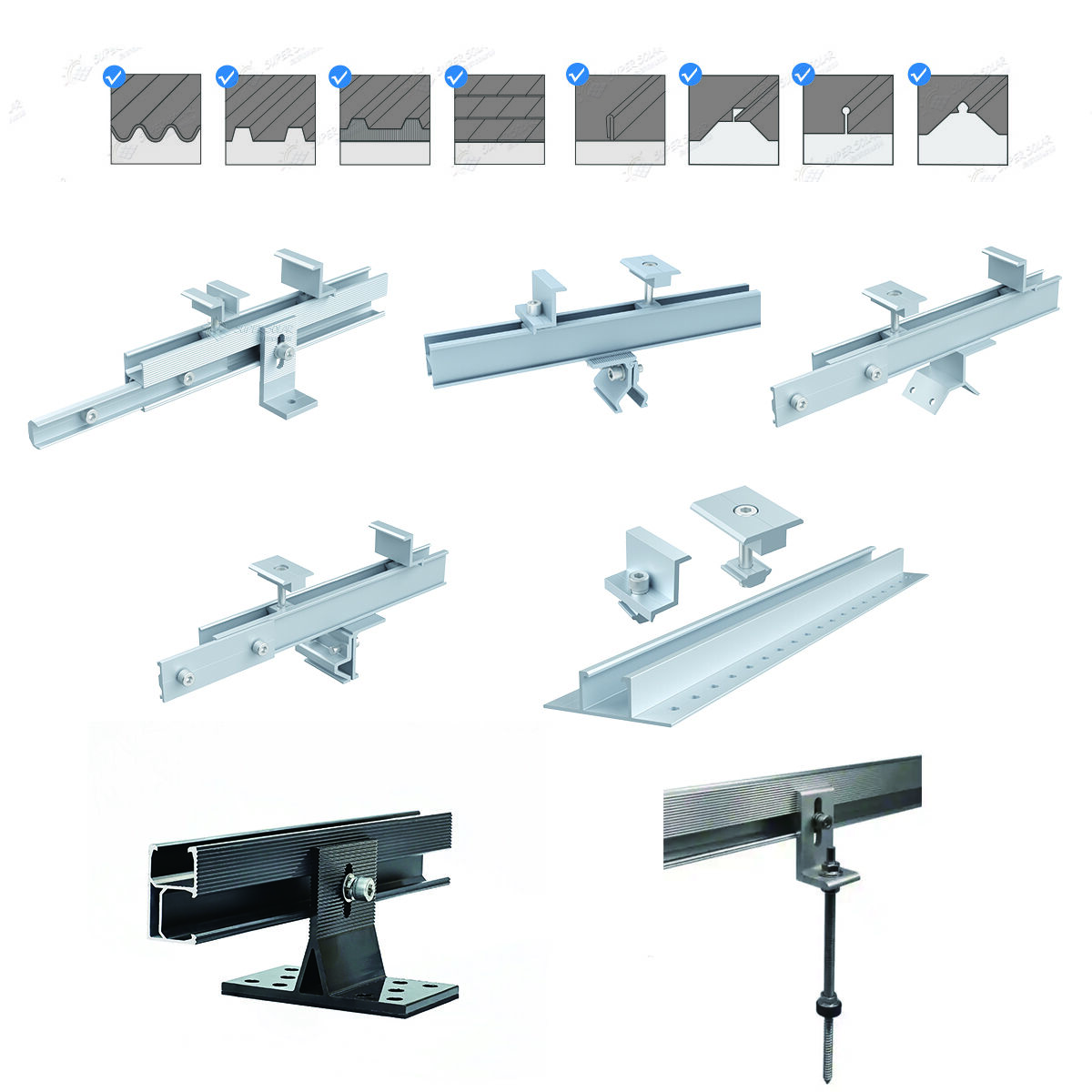
Understanding roof profiles is the first step in selecting a proper solar mounting system.
Standing seam roofs feature raised seams running vertically along the roof. These seams allow the use of non-penetrating solar clamps that grip the seam without drilling.
Key characteristics:
· Ideal for non-penetrating PV mounting
· Excellent waterproof performance
· Common in commercial and industrial buildings
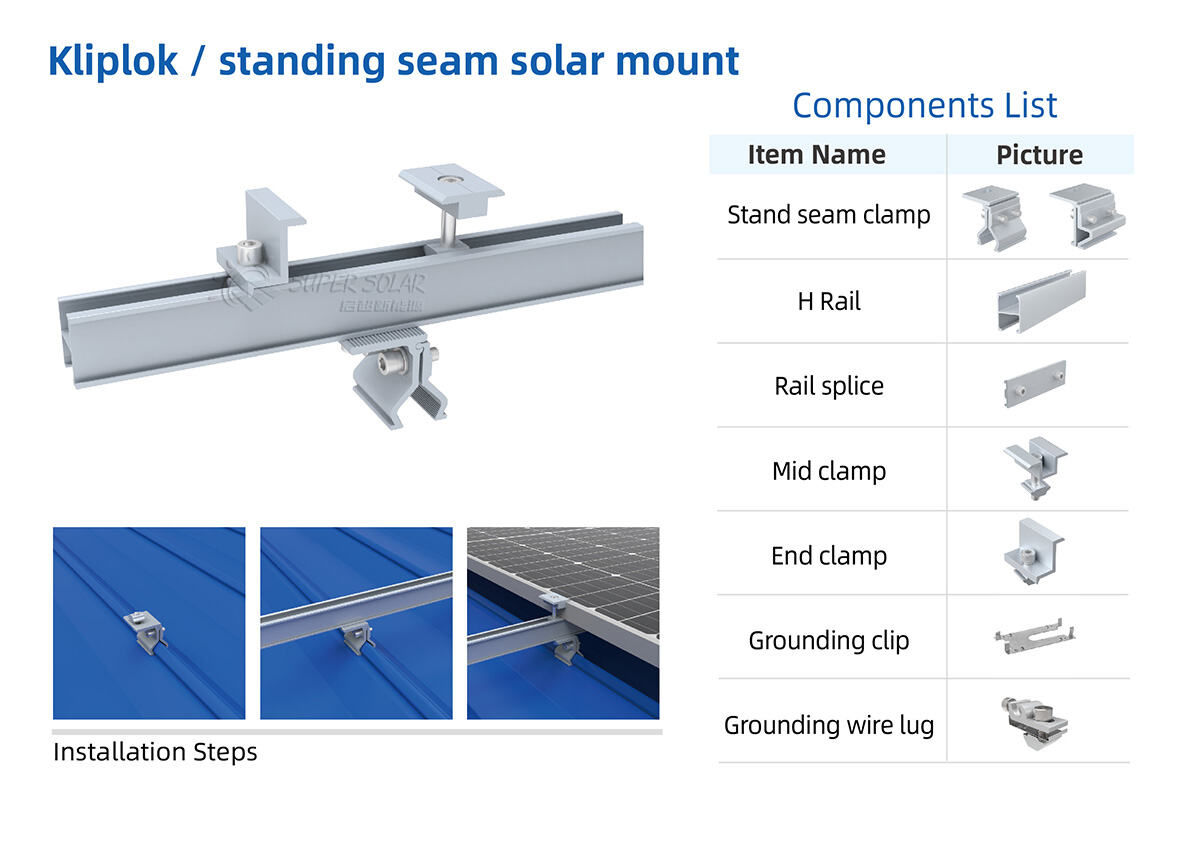
Typical solution: Standing seam solar clamp systems
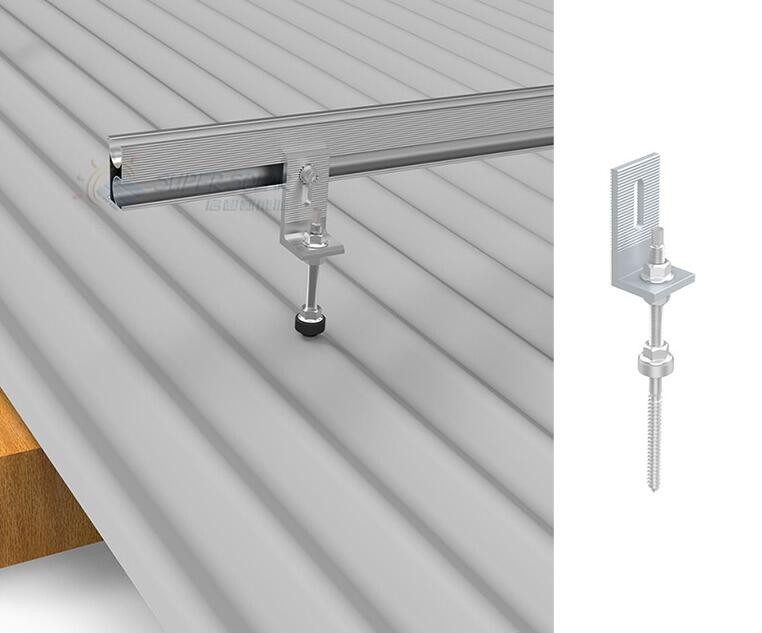
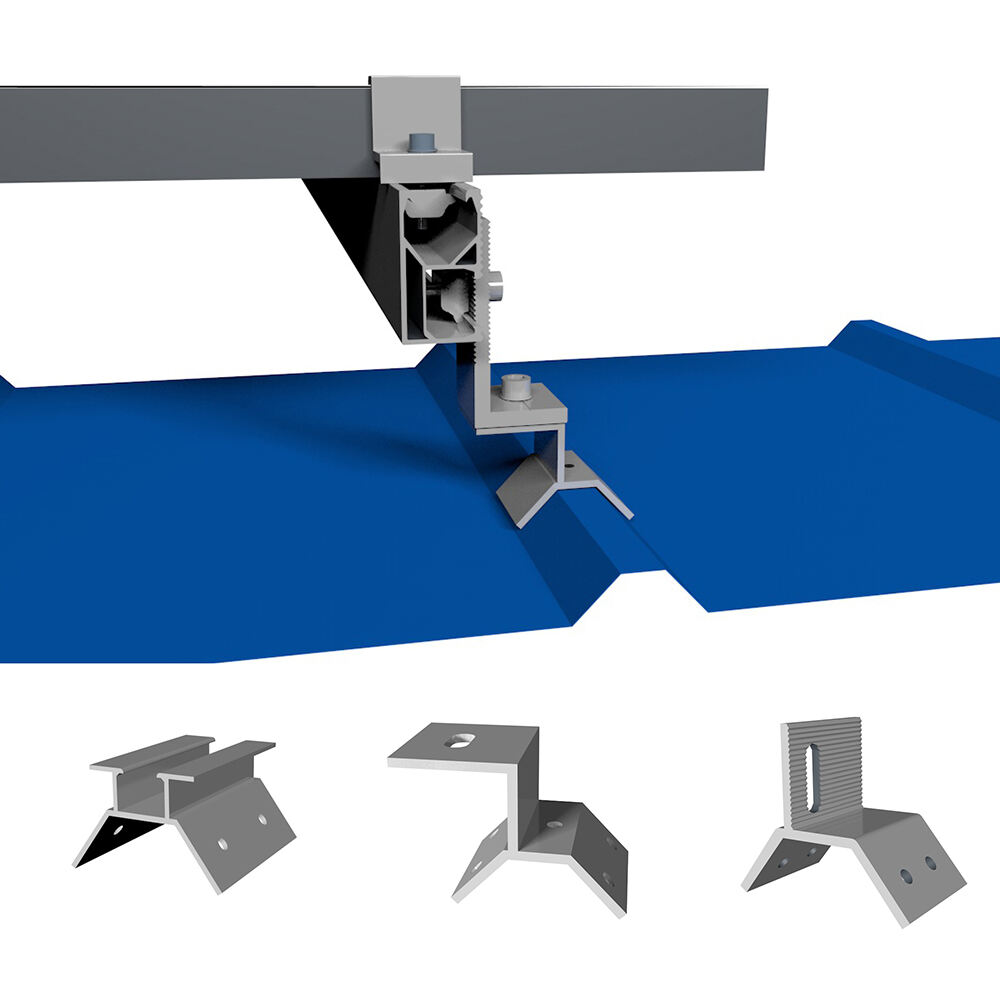
Trapezoidal roofs (also called ribbed or profiled metal roofs) have repeating ridges and valleys. PV mounting typically involves fasteners anchored into purlins through EPDM-sealed screws.
Key characteristics:
· Widely used in industrial facilities
· Requires engineered fastening solutions
· Suitable for rail-based systems
Typical solution: Trapezoidal roof solar mounting with rails or short rails
Corrugated roofs have a wave-like profile and are common in older industrial or agricultural buildings.
Key characteristics:
· Requires careful load distribution
· Waterproofing is critical
· Often uses bracket-and-rail structures
Typical solution: Corrugated roof brackets with sealing fasteners

One of the most common questions from B2B buyers is whether solar mounting will damage the roof.
Used primarily on standing seam roofs, these systems:
· Do not require drilling
· Preserve roof waterproof layers
· Reduce installation time
· Minimize long-term maintenance risks
Standing seam clamps are engineered to transfer loads through the seam structure without compromising roof integrity.
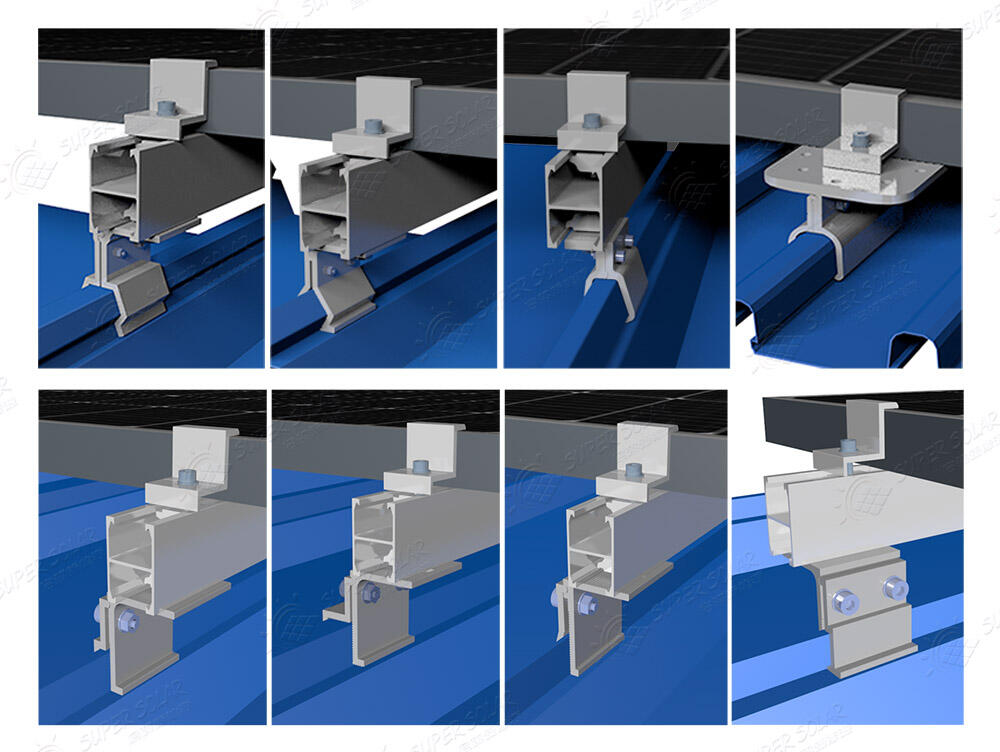
Used on trapezoidal and corrugated roofs, penetrating systems:
· Anchor directly to structural purlins
· Use certified waterproof fasteners
· Require correct torque control and sealing design
When properly engineered, penetrating systems are safe and industry-standard for profiled metal roofs.
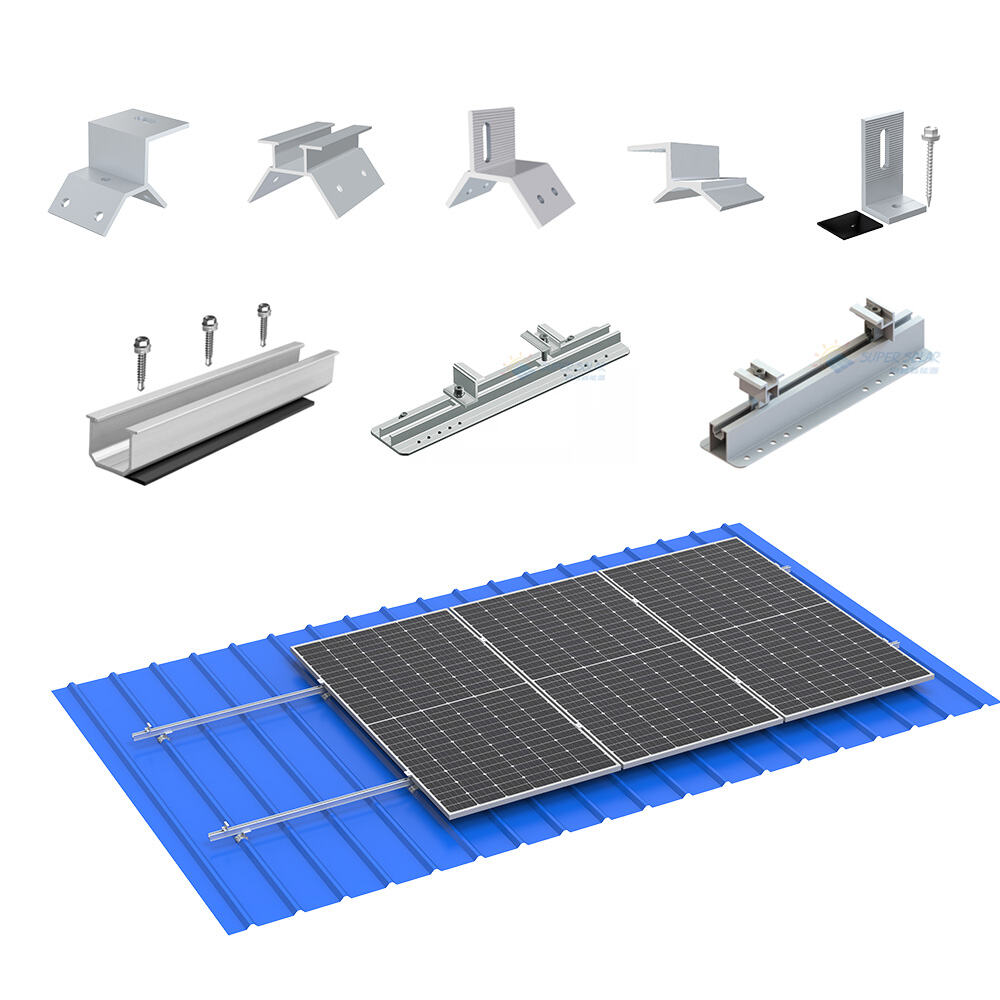
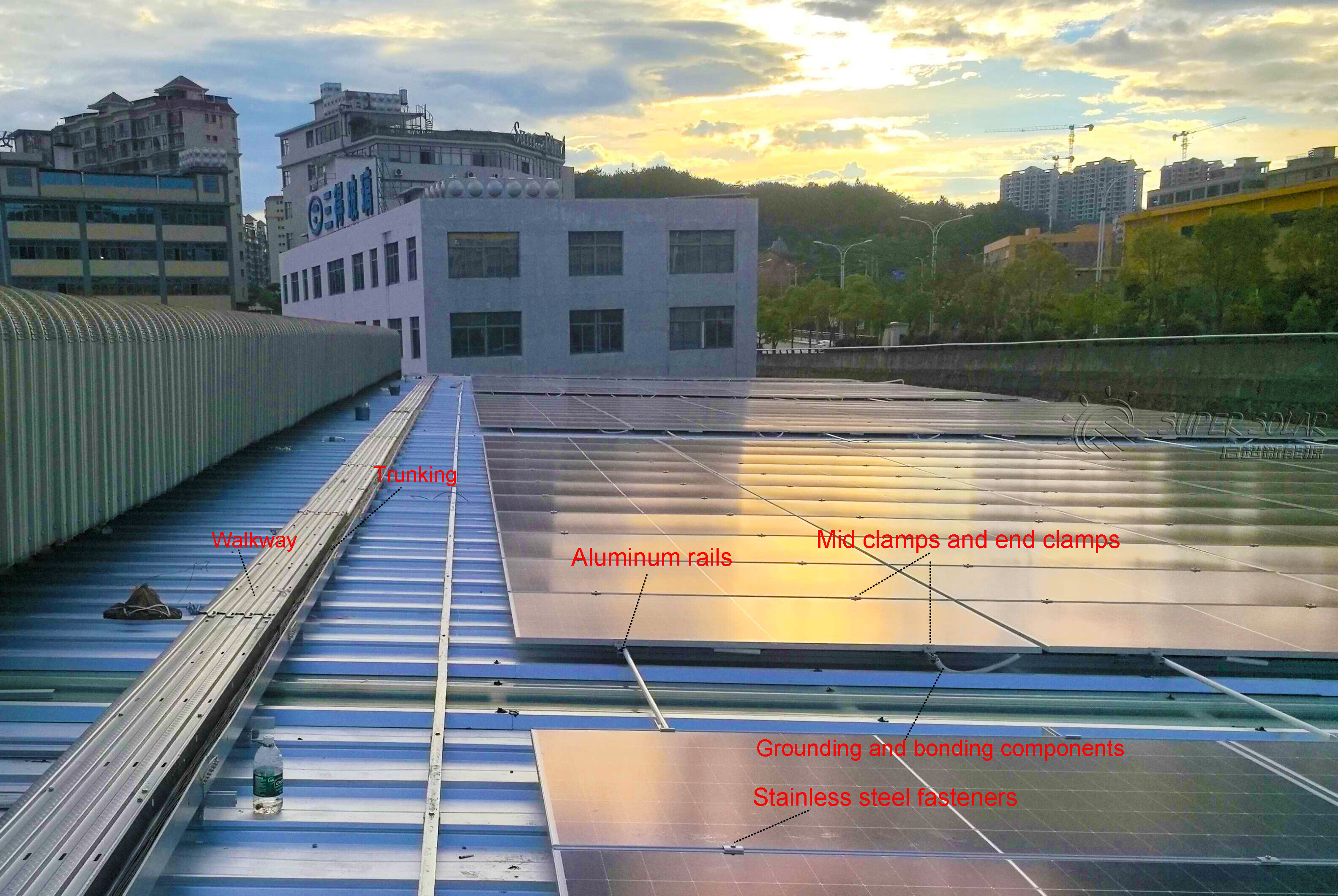
A typical metal roof PV mounting system includes:
· Roof clamps or brackets (profile-specific)
· Aluminum rails or mini-rails
· Mid clamps and end clamps for module fixation
· Stainless steel fasteners
· Grounding and bonding components
System compatibility with module frame thickness, wind zones, and roof material must be verified during design.

Metal roof solar systems must be designed according to project-specific environmental conditions:
· Wind load (uplift and lateral forces)
· Snow load (static and drifting)
· Roof slope and building height
Professional manufacturers provide engineering calculations and test reports to ensure compliance with standards such as EN 1991, ASCE 7, or local building codes.
Avoiding these mistakes can significantly reduce project risk:
· Treating all metal roofs as identical
· Using generic clamps without profile verification
· Ignoring roof manufacturer warranty requirements
· Underestimating wind load in edge and corner zones
Selecting a system specifically designed for the target roof type is essential.
When evaluating suppliers or systems, B2B buyers should consider:
· Roof profile compatibility
· Non-penetrating vs penetrating requirements
· Structural certifications and test reports
· Installation efficiency
· Long-term durability and corrosion resistance
A professional manufacturer should support not only products, but also system design and technical documentation.

Metal roof solar mounting systems are not one-size-fits-all solutions. Understanding roof types, load requirements, and mounting methods is critical to building safe and durable PV projects.
By choosing purpose-designed mounting systems and working with experienced manufacturers, installers and distributors can ensure long-term performance while protecting roof integrity.