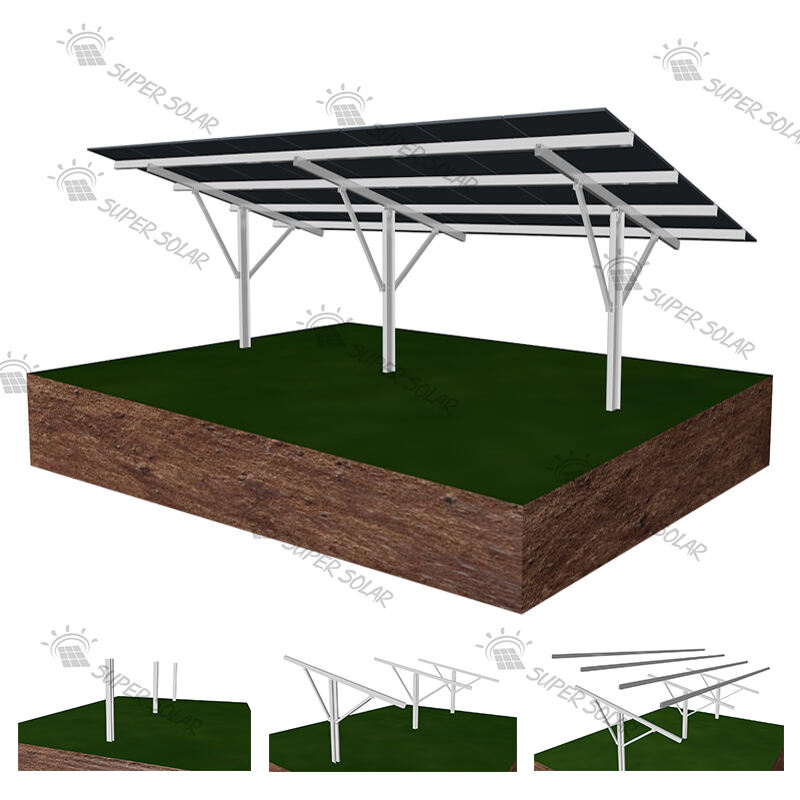
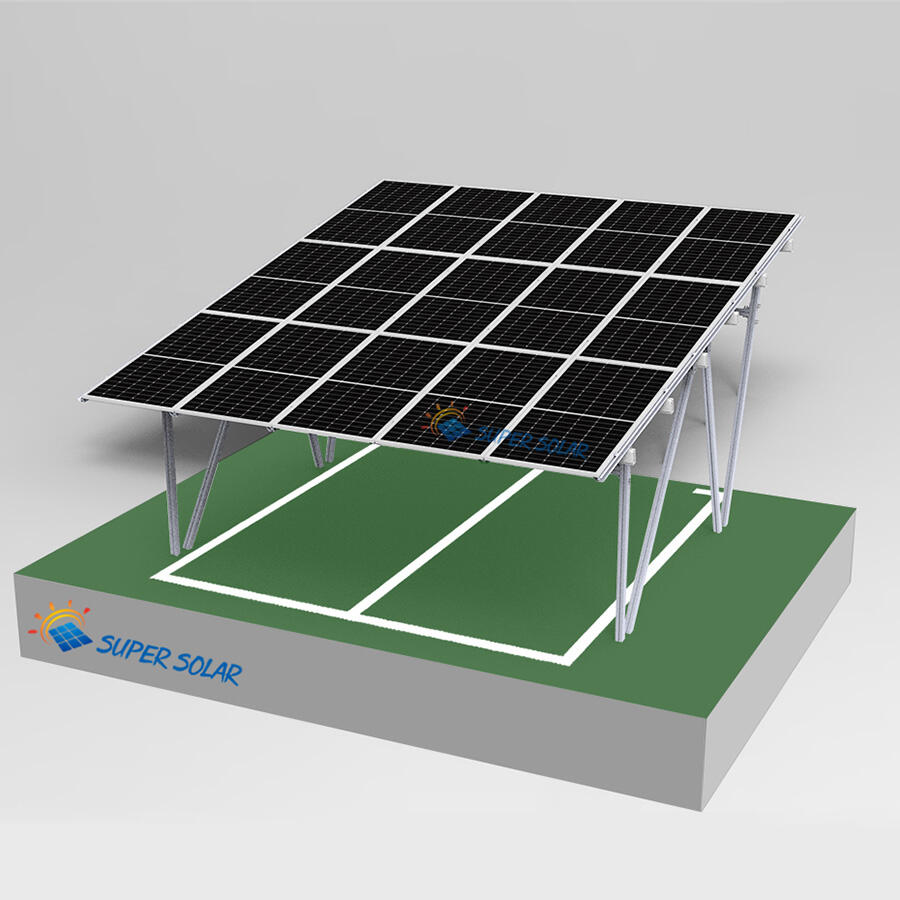
Продвинутая Технология Генерации Энергии
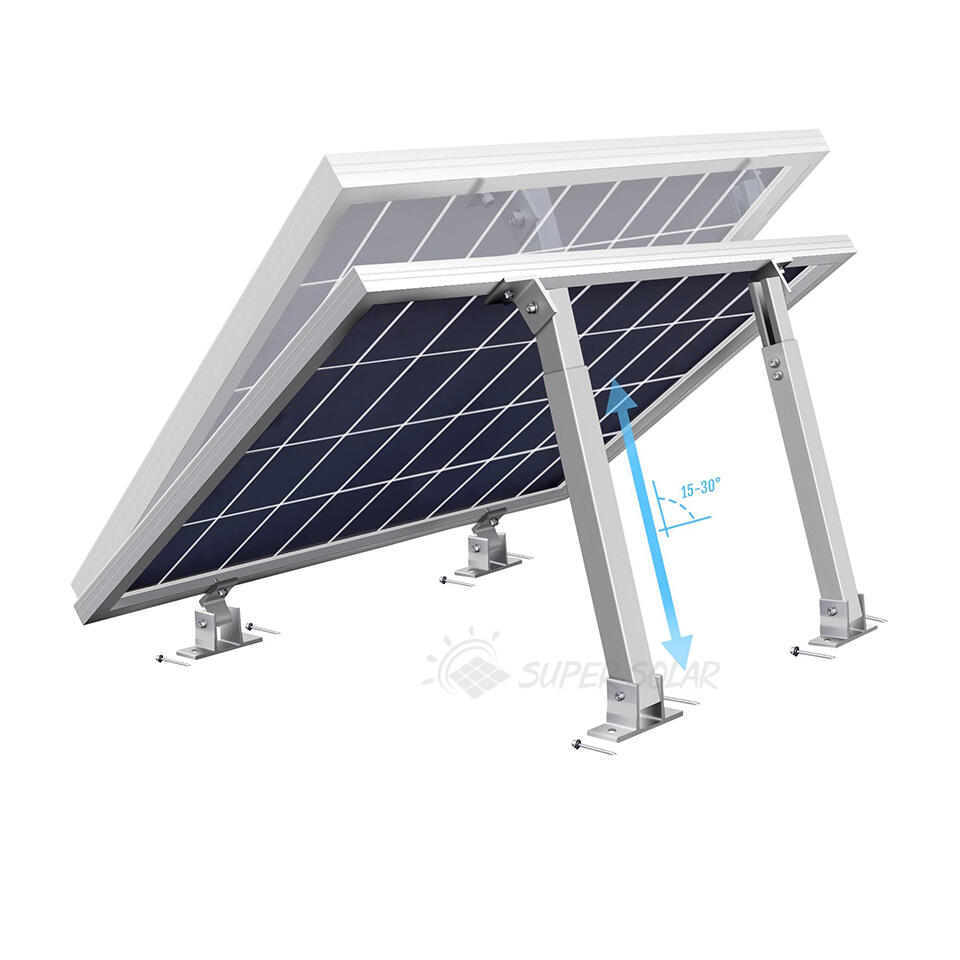
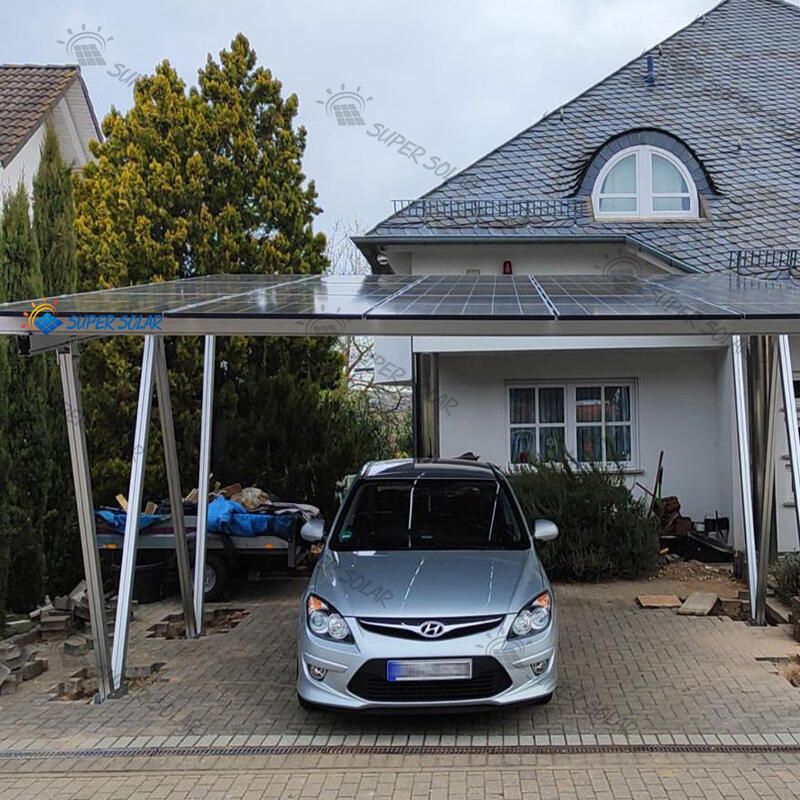
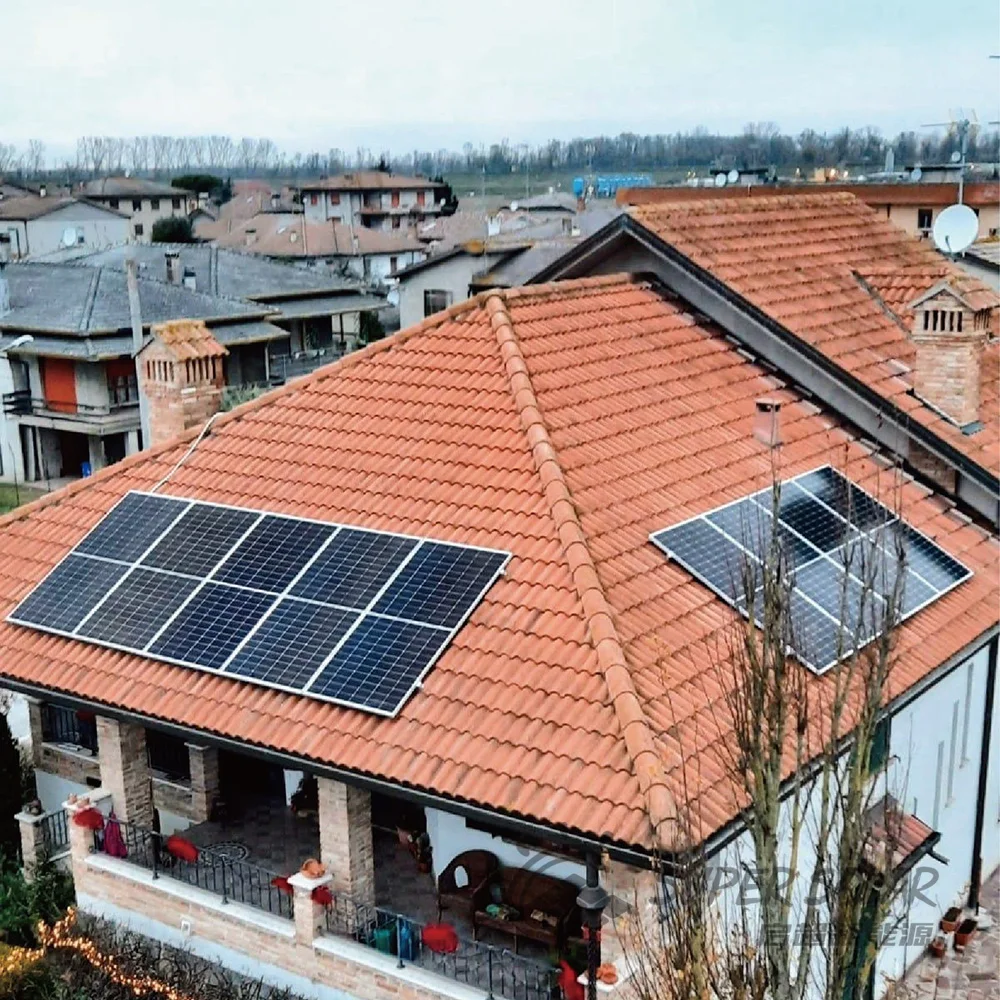
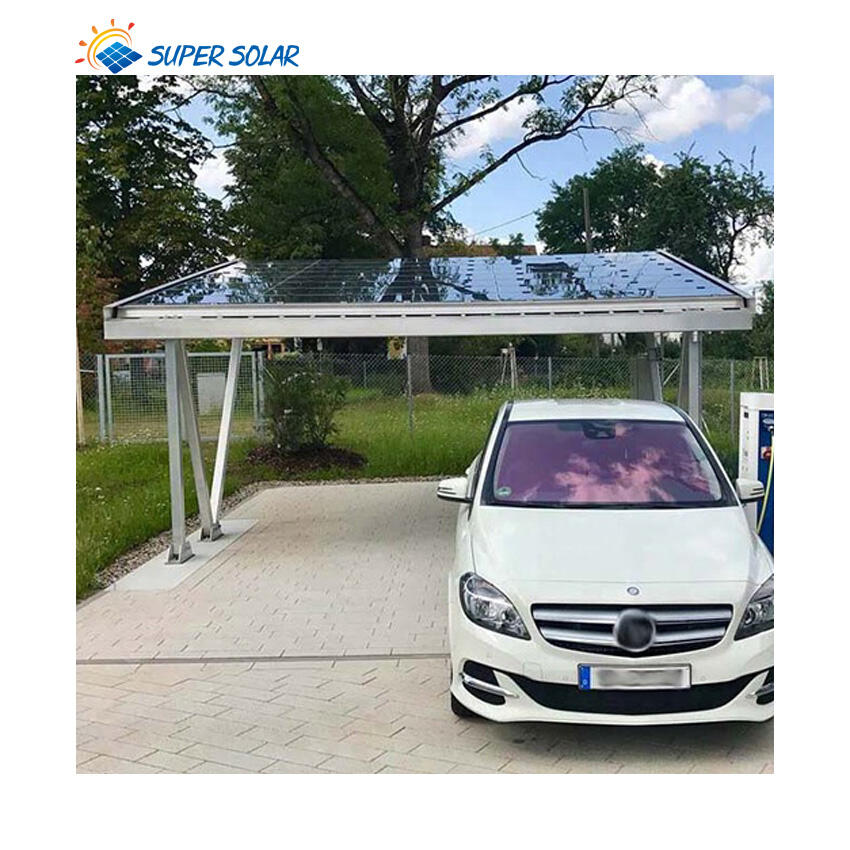
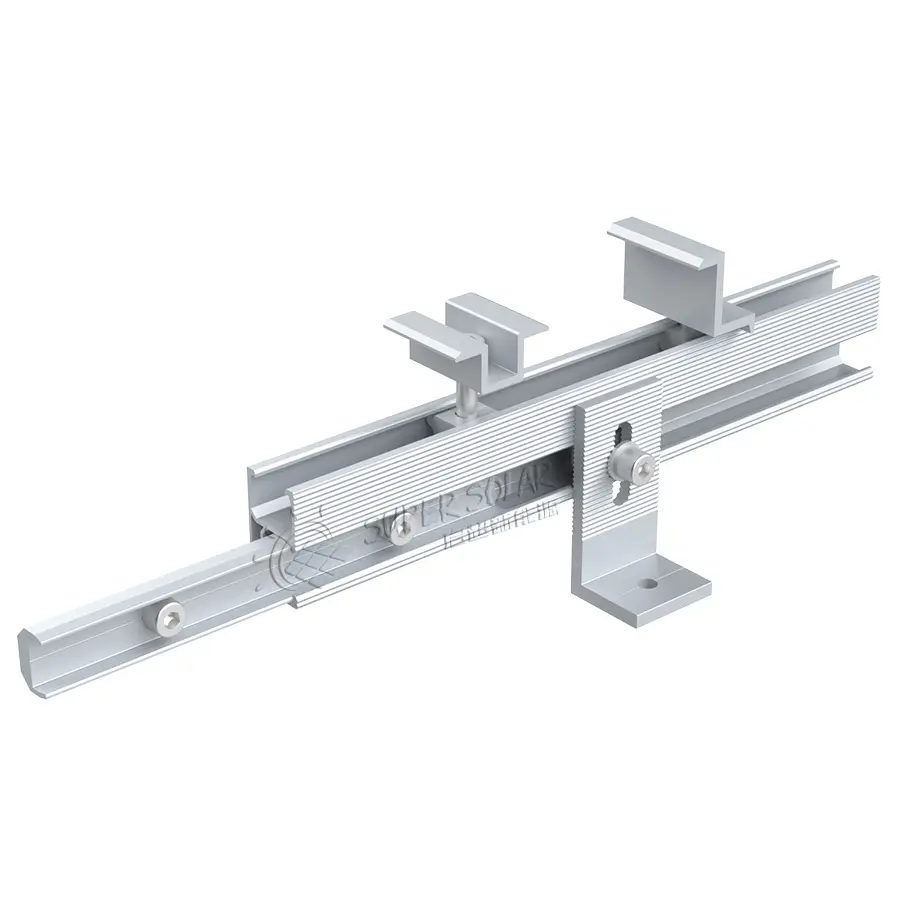
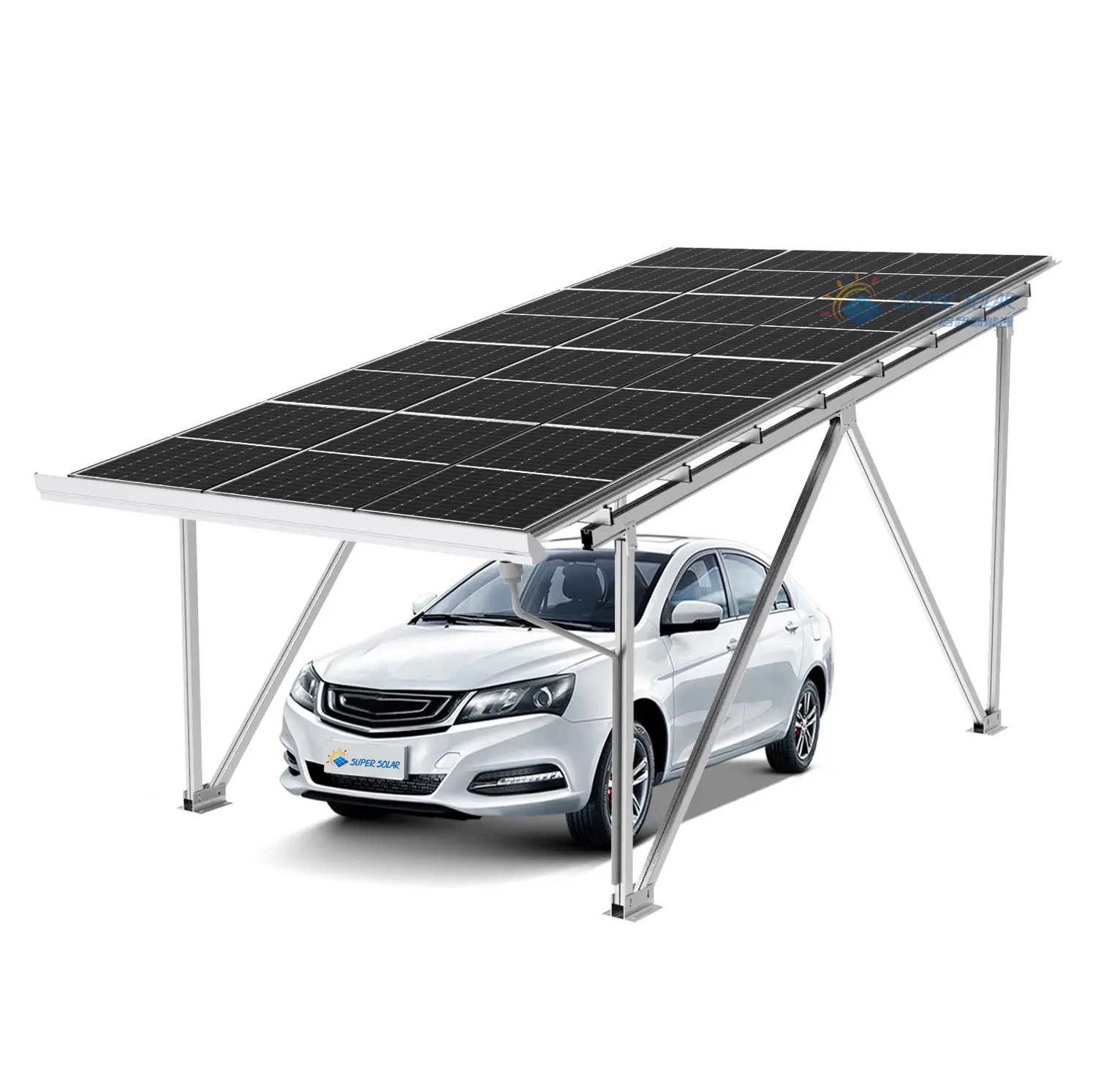
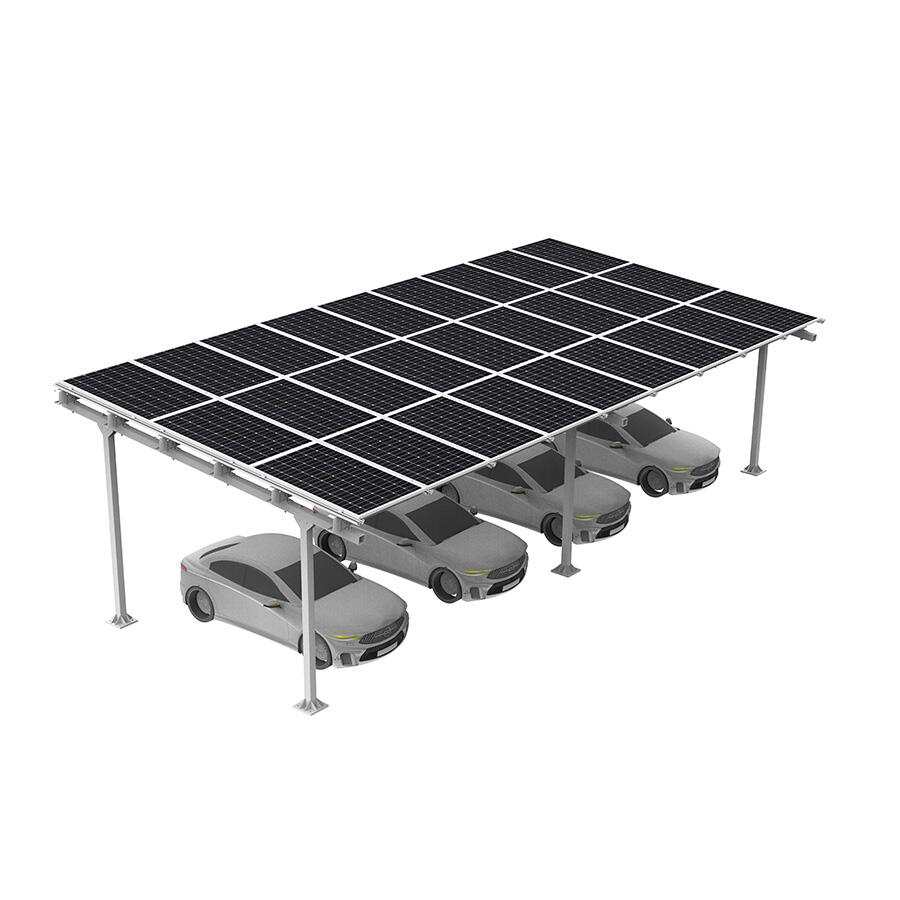
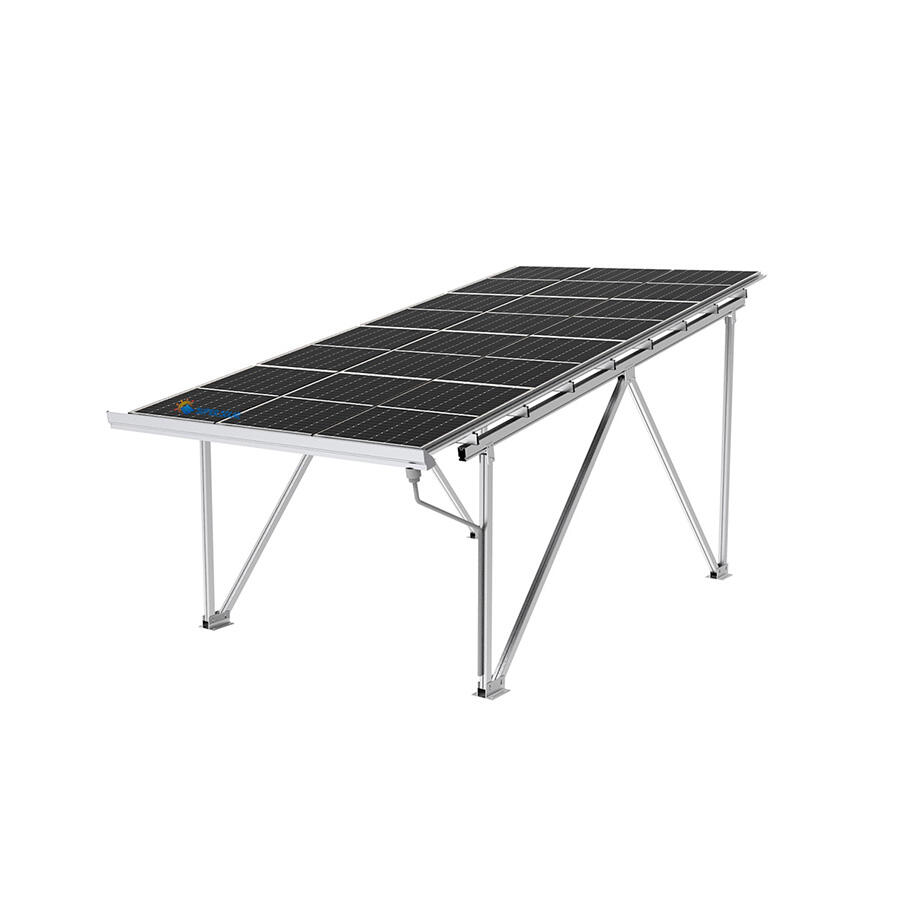
Солнечные навесы для жилых помещений включают передовые фотогальванические технологии, которые максимизируют выработку энергии за счёт оптимального размещения панелей, современных инверторных систем и возможностей умного мониторинга, обеспечивающих пиковую производительность на протяжении всего жизненного цикла системы. Конфигурация установки на повышенной высоте обеспечивает превосходное воздействие солнечного света по сравнению со многими крышами, особенно в районах, где жилые крыши ориентированы неоптимально или подвергаются затенению от деревьев, соседних зданий или природных объектов, ограничивающих доступ солнечного света. Современные установки используют высокоэффективные монокристаллические панели мощностью 300–400 Вт каждая, в сочетании с оптимизаторами мощности или микропреобразователями, которые максимизируют сбор энергии с каждой отдельной панели, минимизируя влияние частичного затенения, которое может значительно снизить общую производительность системы. Конструктивный дизайн позволяет точно регулировать угол наклона, оптимизируя сезонную выработку энергии, а некоторые системы оснащены механизмами слежения, которые следуют за траекторией солнца в течение дня для максимального сбора энергии. Умные инверторы обеспечивают мониторинг производительности в реальном времени, управление подключением к сети и функции безопасности, включая возможность быстрого отключения, соответствующие действующим нормам электробезопасности и требованиям энергосбытовых компаний. Солнечные навесы для жилых помещений, как правило, вырабатывают от 4000 до 12 000 киловатт-часов в год в зависимости от географического положения, размера системы и местных погодных условий, обеспечивая значительную выработку энергии, которая часто превышает потребление домохозяйства, создавая возможности для продажи избыточной электроэнергии энергосбытовым компаниям через программы сетевого учёта. Модульная конфигурация панелей позволяет расширять систему по мере роста потребностей в энергии или наличия бюджета, при этом дополнительные панели легко интегрируются в существующие конструкции без необходимости полной реконструкции или значительных изменений в электрической инфраструктуре. Продвинутые системы мониторинга предоставляют детализированную аналитику производительности через мобильные приложения и веб-порталы, позволяя домовладельцам отслеживать выработку энергии, выявлять потенциальные проблемы и оптимизировать режимы потребления для максимальной финансовой выгоды. Интеграция технологий предусматривает возможность будущих усовершенствований, таких как системы хранения энергии в аккумуляторах, станции зарядки электромобилей и автоматизация «умного дома», что создаёт комплексные экосистемы управления энергией. Качественные компоненты, подкреплённые всесторонними гарантиями, обеспечивают надёжную работу в течение 25–30 лет при минимальных требованиях к обслуживанию и предсказуемом снижении производительности, что позволяет точно планировать финансы на долгосрочной основе и рассчитывать окупаемость инвестиций.