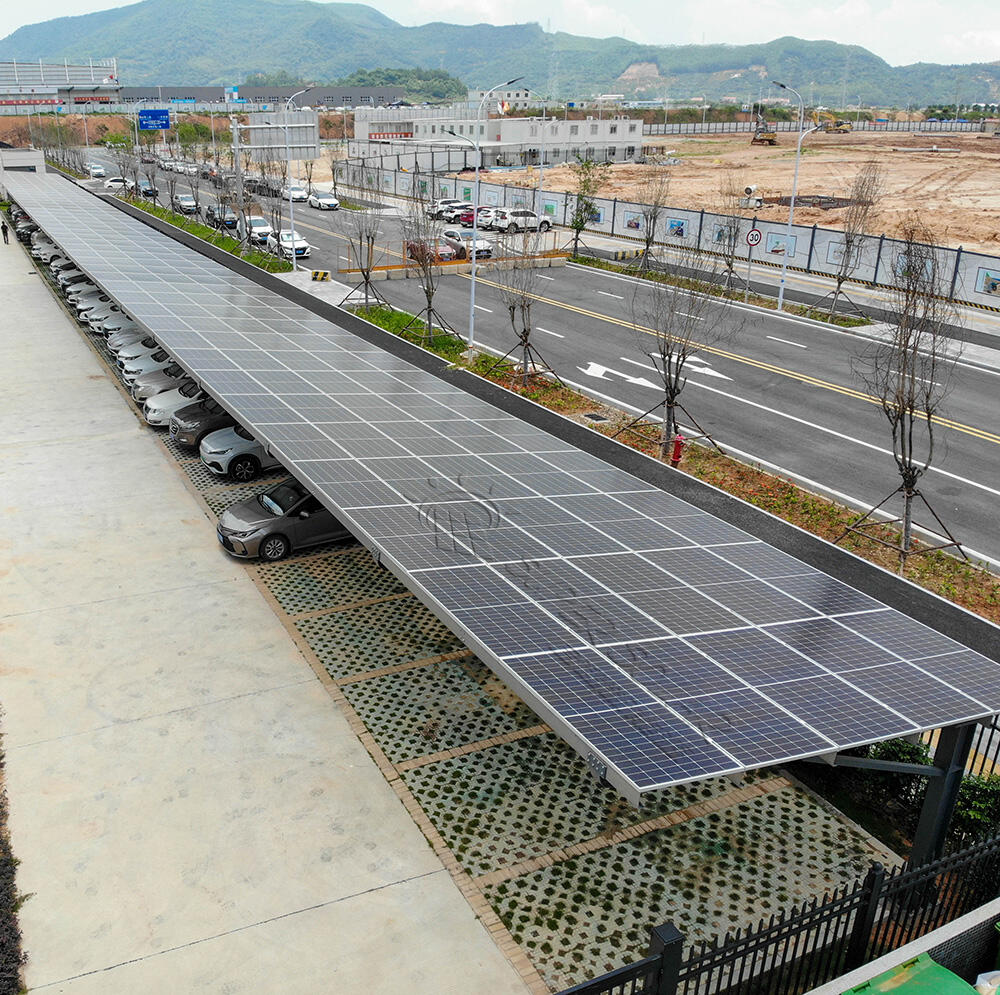
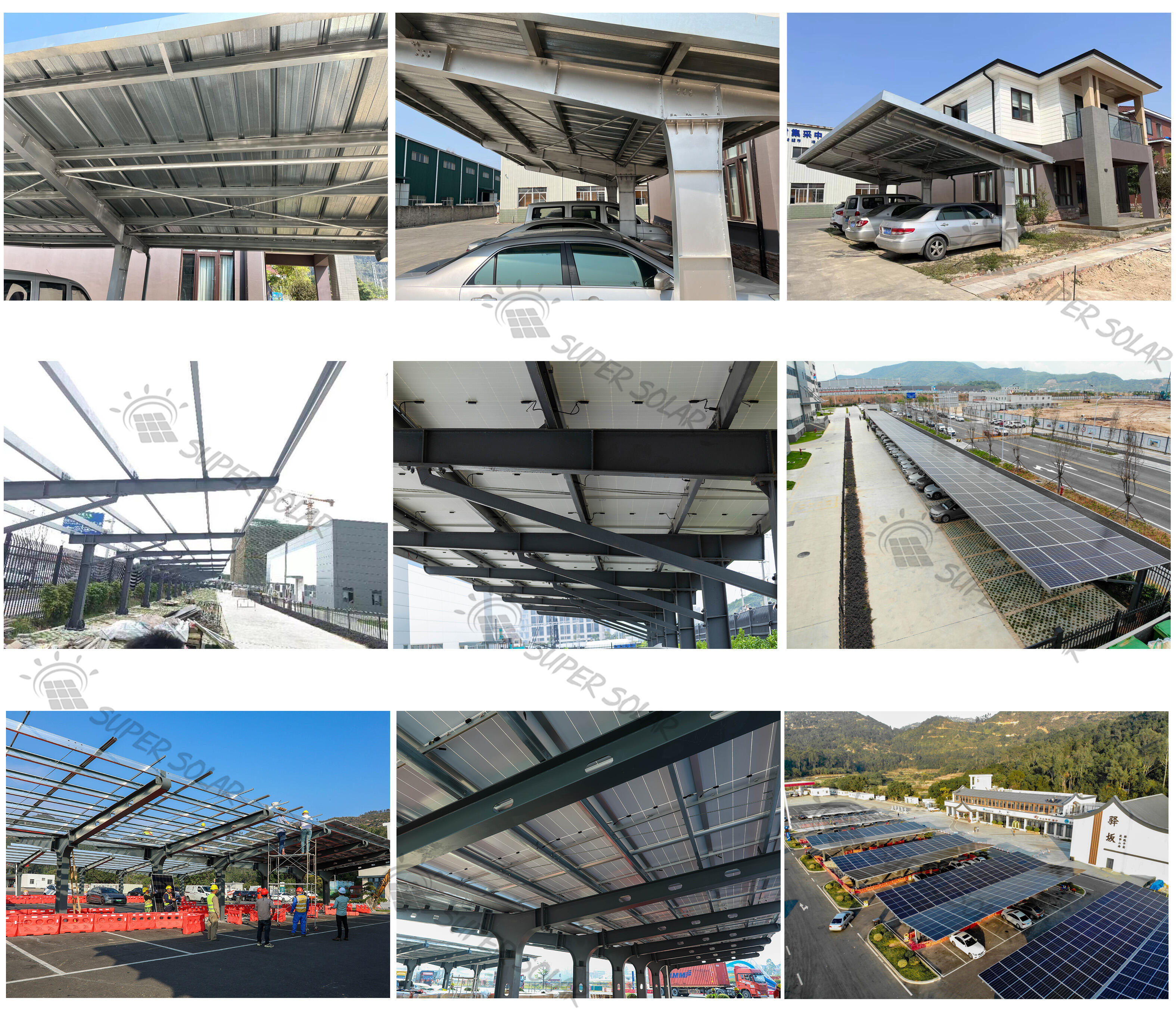
Commercial Parking Scenarios and the Role of PV Carport Systems
For commercial property owners, parking lots are often underutilized assets. Large surface areas generate no direct revenue while still requiring ongoing maintenance. A pv carport transforms these passive spaces into productive energy infrastructure, combining vehicle shelter with on-site solar generation. In recent years, commercial parking projects have increasingly evaluated pv carport solutions not only from an energy perspective, but also as part of broader sustainability, cost-control, and branding strategies.

Unlike rooftop systems, a pv carport must simultaneously satisfy structural safety, waterproofing performance, traffic circulation, and aesthetic requirements. These constraints make design decisions more complex, especially for shopping centers, office parks, logistics hubs, hospitals, and industrial campuses. Buyers are rarely asking what a pv carport is; instead, they want to know whether it is waterproof, how much capacity it can host, how quickly it pays back, and whether it can integrate with storage or EV charging.
From a manufacturer’s standpoint, the value lies in offering scenario-based solutions rather than standardized frames. Parking layouts, vehicle types, local climate, and energy consumption patterns all influence the optimal pv carport configuration. Addressing these factors at the design stage improves ROI predictability and reduces downstream modification costs.
Single-Row, Double-Row, and Custom Carport Configurations
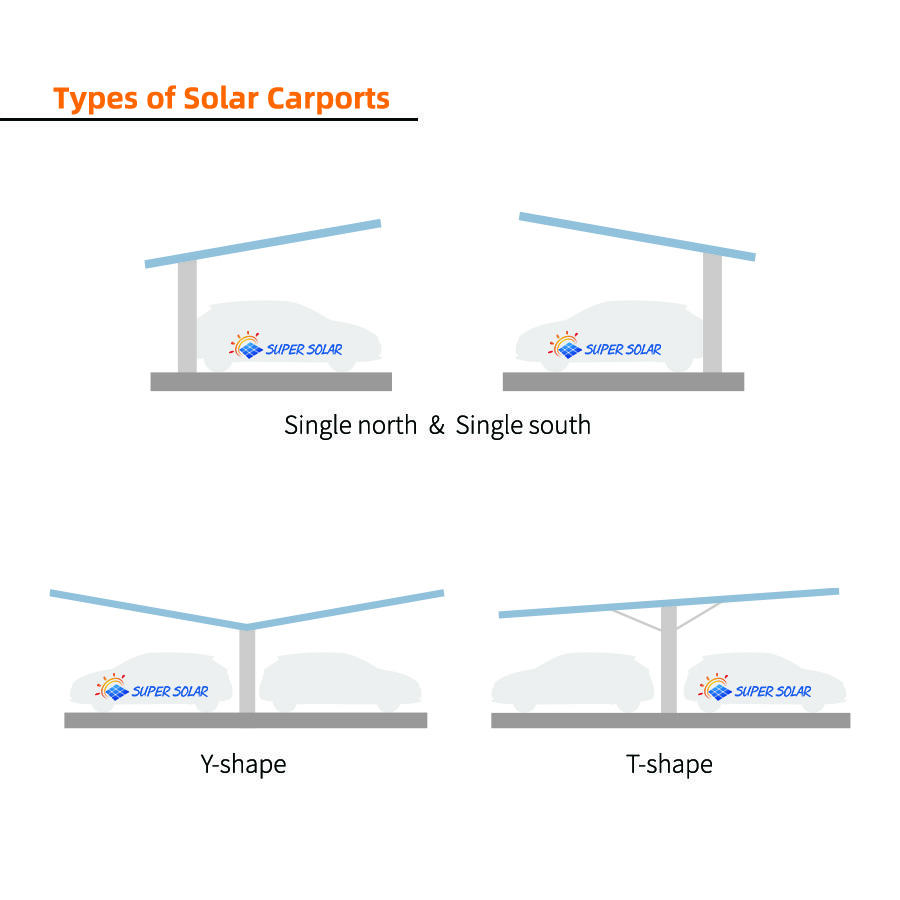
Commercial parking lots vary widely in layout and scale. Selecting the right pv carport configuration directly affects installation efficiency, shading coverage, and total installed capacity. A clear understanding of structural options helps project owners match design choices with site conditions and investment goals.
Single-Row PV Carport Applications
Single-row pv carport structures are commonly used along perimeter parking zones, internal drive aisles, or areas with limited space. They typically serve one row of parking bays and offer flexible orientation options. This configuration is well suited for sites where vehicle circulation must remain unobstructed or where underground utilities restrict foundation placement.
From a capacity standpoint, single-row designs provide moderate installed power density. Their simplicity allows faster installation and easier phasing for projects with budget constraints. In many retail or office environments, single-row pv carport solutions are used to test feasibility before scaling to larger deployments.
Double-Row PV Carport Structures
Double-row pv carport systems cover two opposing parking rows with a shared structural spine. This design maximizes module density and improves land-use efficiency, making it popular for large commercial lots. By reducing the number of columns per kilowatt installed, double-row structures often achieve better cost performance at scale.
Structural design is more demanding due to wider spans and higher wind loads. Manufacturers with strong engineering capabilities can optimize steel sections or aluminum profiles to balance stiffness and material usage. For clients focused on maximizing installed capacity and long-term returns, double-row pv carport layouts are often the preferred solution.
Custom Carport Designs for Complex Sites
Not all parking lots follow standard layouts. Irregular geometries, mixed vehicle sizes, height restrictions, or architectural requirements may necessitate custom pv carport solutions. Customization can involve variable spans, asymmetric layouts, or integration with existing buildings and landscape features.
While custom designs typically require more upfront engineering effort, they allow commercial owners to unlock solar potential in otherwise challenging areas. A manufacturer-led design approach ensures that customization does not compromise structural integrity, waterproofing performance, or maintenance accessibility.
Waterproof Versus Non-Waterproof PV Carport Structures
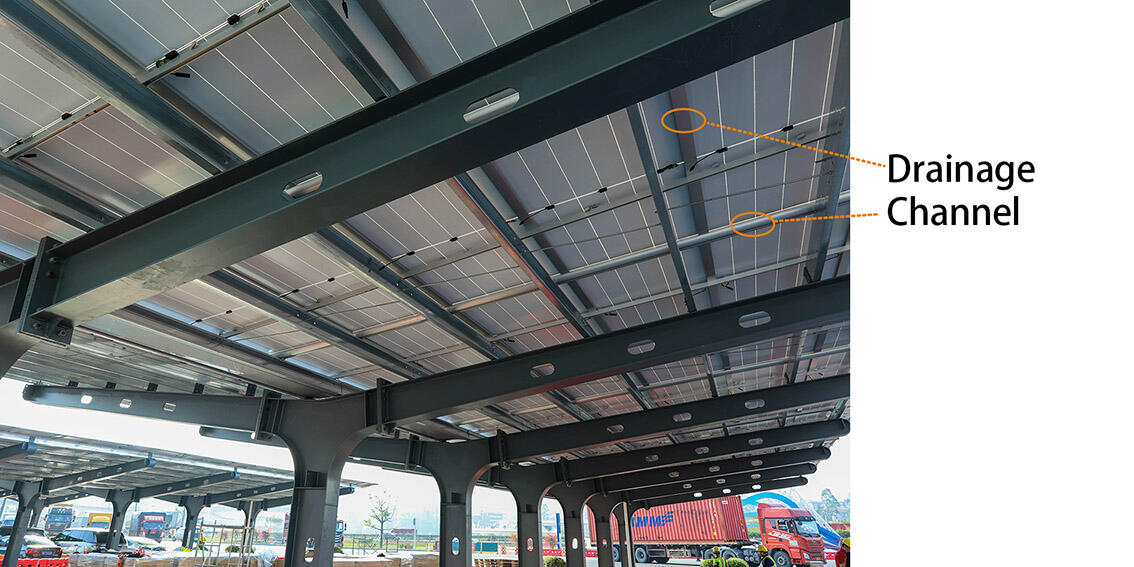

One of the most frequent decision points in pv carport projects is whether to choose a waterproof or non-waterproof structure. This choice influences user experience, construction complexity, and overall project economics.
Non-Waterproof Carport Structures and Use Cases
Non-waterproof pv carport systems rely on standard module installation without sealed drainage layers. Rainwater passes through module gaps and falls beneath the structure. This approach reduces material and installation costs and is often acceptable in climates with low rainfall or in applications where vehicle protection from rain is not a priority.
From a structural standpoint, non-waterproof systems are simpler and lighter. They are commonly used in industrial or logistics environments where the primary objective is energy generation rather than user comfort. However, water runoff management must still be considered to avoid erosion or pooling.
Fully Waterproof PV Carport Solutions
Waterproof pv carport systems integrate sealing components, drainage channels, and sloped surfaces to prevent leakage. These designs provide full weather protection for vehicles and pedestrians, making them suitable for commercial and public-facing locations.
Waterproofing adds complexity to both design and installation. Precision in module alignment, sealing materials, and drainage planning is essential. Manufacturers experienced in waterproof pv carport projects can deliver systems that maintain long-term performance without frequent maintenance issues. For many commercial owners, the added comfort and perceived quality justify the higher initial investment.
Cost and Performance Trade-Offs
The choice between waterproof and non-waterproof designs should align with site usage and business objectives. While waterproof systems increase upfront costs, they can enhance property value, user satisfaction, and potential ancillary revenue streams. Non-waterproof options, by contrast, prioritize cost efficiency and rapid deployment.
Steel Versus Aluminum Structural Systems
Material selection is another critical factor influencing pv carport durability, cost, and appearance. Steel and aluminum structures each offer distinct advantages depending on project requirements.
Steel PV Carport Structures
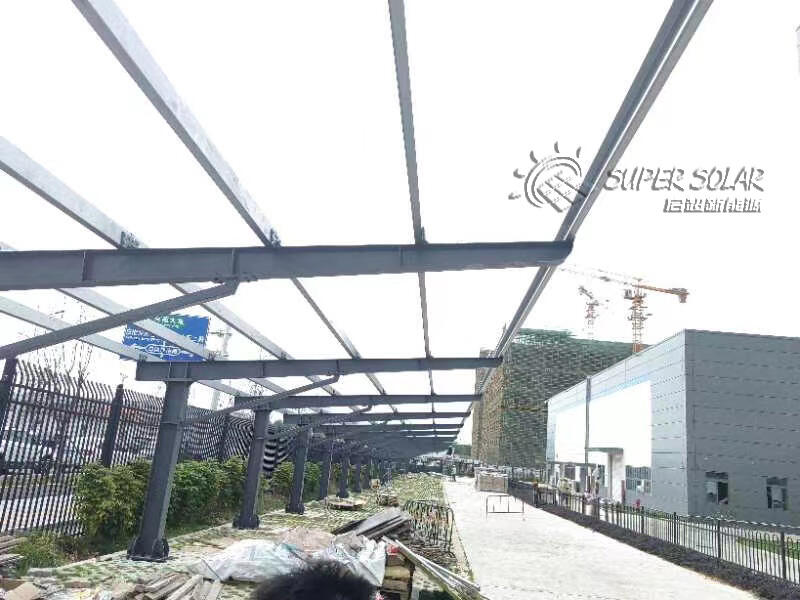

Steel is widely used in pv carport construction due to its high strength and cost-effectiveness. It allows longer spans and higher load capacity, which is beneficial for double-row and large-scale installations. Galvanized or coated steel provides reliable corrosion resistance when properly specified.
Steel structures are well suited for projects prioritizing structural robustness and budget control. Their higher weight, however, requires careful foundation design and installation planning. For many commercial parking lots, steel remains the default choice due to its proven performance and scalability.
Aluminum PV Carport Systems
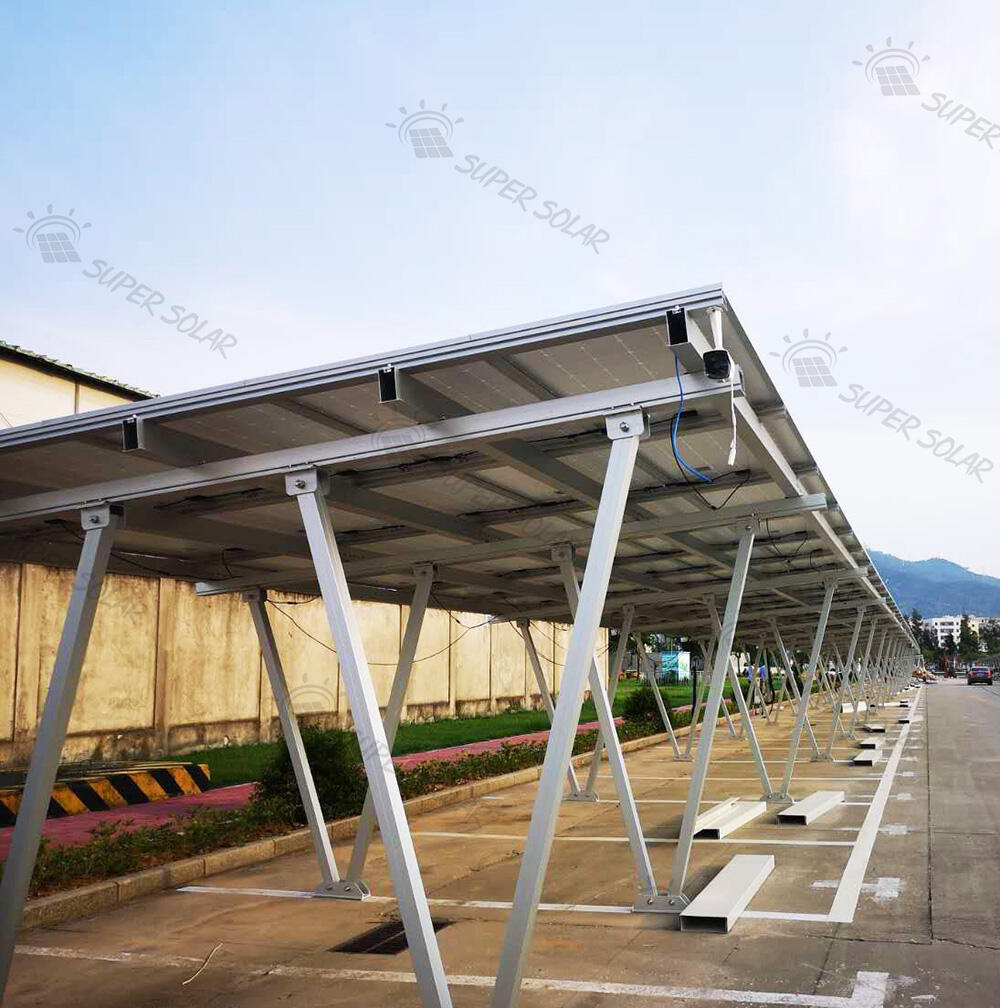

Aluminum pv carport structures offer advantages in corrosion resistance, lighter weight, and refined appearance. These properties make aluminum attractive for coastal environments, premium commercial developments, or sites with strict architectural guidelines.
While aluminum typically carries higher material costs, reduced installation effort and lower long-term maintenance can offset this difference. Manufacturers with aluminum fabrication expertise can deliver precise, modular designs that integrate seamlessly with modern commercial environments.
Matching Material Choice to Project Goals
The decision between steel and aluminum should consider environmental conditions, aesthetic expectations, installation constraints, and lifecycle cost. A manufacturer that provides both options can offer objective recommendations based on site-specific priorities rather than material limitations.
Installed Capacity, Payback Period, and ROI Analysis

For decision-makers, financial performance remains the ultimate benchmark. A pv carport project must demonstrate clear economic value alongside its functional benefits.
Installed Capacity Optimization
Installed capacity depends on parking layout, carport configuration, module selection, and tilt angle. Double-row and custom designs generally enable higher capacity per square meter, improving energy yield potential. Accurate layout planning ensures that structural elements do not unnecessarily reduce usable module area.
Manufacturers who provide preliminary capacity simulations can help clients understand realistic output expectations before committing to detailed design.
Cost Structure and Investment Considerations
Project costs typically include structure, modules, foundations, electrical components, and installation. Waterproofing, material choice, and customization level significantly influence total investment. Transparent cost breakdowns help commercial owners evaluate trade-offs between upfront expenditure and long-term benefits.
In many regions, incentives, net metering policies, or corporate sustainability targets further enhance project viability. These factors should be considered as part of a holistic ROI assessment.
Payback Period and Long-Term Returns
Payback periods for pv carport projects vary depending on electricity prices, self-consumption rates, and system scale. Commercial parking lots with daytime energy demand often achieve favorable returns due to high on-site usage.
Beyond direct energy savings, pv carport installations can reduce heat island effects, improve user experience, and support ESG objectives. These indirect benefits, while harder to quantify, contribute to the overall return profile.
Integration with Energy Storage and EV Charging

Modern commercial parking projects increasingly look beyond standalone solar generation. A pv carport can serve as a foundation for integrated energy solutions.
Battery storage enables load shifting and peak shaving, improving energy utilization efficiency. EV charging infrastructure leverages the carport’s proximity to vehicles, creating additional value streams. When designed together, these systems can share electrical infrastructure and reduce incremental costs.
Manufacturers capable of coordinating structural and electrical interfaces simplify integration and future expansion. This flexibility is particularly important as energy demand patterns evolve.
Scenario-Based Solutions as a Project Strategy
Successful pv carport projects are rarely one-size-fits-all. Retail centers, office campuses, logistics hubs, and public facilities each present distinct usage patterns and priorities. A scenario-based approach aligns design choices with real-world operation.
By combining configuration selection, waterproofing strategy, material choice, and energy integration into cohesive solutions, manufacturers can address both technical and commercial concerns. This approach supports informed decision-making and reduces project risk.
For commercial owners evaluating pv carport investments, collaboration at the early design stage is often the most effective way to achieve predictable performance and returns.
FAQ
Is a pv carport suitable for all commercial parking lots
Most commercial parking lots can accommodate a pv carport, but feasibility depends on layout, soil conditions, local regulations, and energy demand. Site assessment is essential to determine optimal configuration and capacity.
How important is waterproofing for a pv carport project
Waterproofing is critical in locations where vehicle protection and user comfort are priorities. In purely industrial settings, non-waterproof designs may be sufficient and more cost-effective.
Can a pv carport system be combined with EV charging and storage
Yes, pv carport systems are well suited for integration with EV chargers and battery storage. Early coordination ensures efficient electrical design and scalability.
What information is needed to evaluate ROI accurately
Key inputs include parking layout drawings, local electricity prices, expected self-consumption rates, climate data, and structural preferences. Sharing this information allows for more accurate capacity and payback estimates.
Table of Contents
- Commercial Parking Scenarios and the Role of PV Carport Systems
- Single-Row, Double-Row, and Custom Carport Configurations
- Waterproof Versus Non-Waterproof PV Carport Structures
- Steel Versus Aluminum Structural Systems
- Installed Capacity, Payback Period, and ROI Analysis
- Integration with Energy Storage and EV Charging
- Scenario-Based Solutions as a Project Strategy
- FAQ
- Is a pv carport suitable for all commercial parking lots
- How important is waterproofing for a pv carport project
- Can a pv carport system be combined with EV charging and storage
- What information is needed to evaluate ROI accurately



