Solar Mounting Systems
Contact Us
- Building A06, Jimei Software Park, Xiamen, China
- +86-592-6683155
- [email protected]
This article is part of our standard mini rail selection guide. For general application criteria, load considerations, and system comparison, please refer to the [Solar Mini Rail Selection Guide].
This guide is written for EPC contractors, structural engineers, and professional installers who are evaluating whether a solar mini rail system can be safely used in high wind zones.
High wind projects require a more conservative and engineering-driven selection process. This document explains when mini rails are feasible, when they are not, and how risks should be managed.
Yes — but only under specific conditions.
Solar mini rail systems can be applied in high wind regions if and only if:
Roof structure and metal sheet strength are verified
Fastener pull-out and pull-over resistance are confirmed
System layout is based on local wind load standards
Installation quality is strictly controlled
If these conditions cannot be met, a full rail system is usually the safer option.
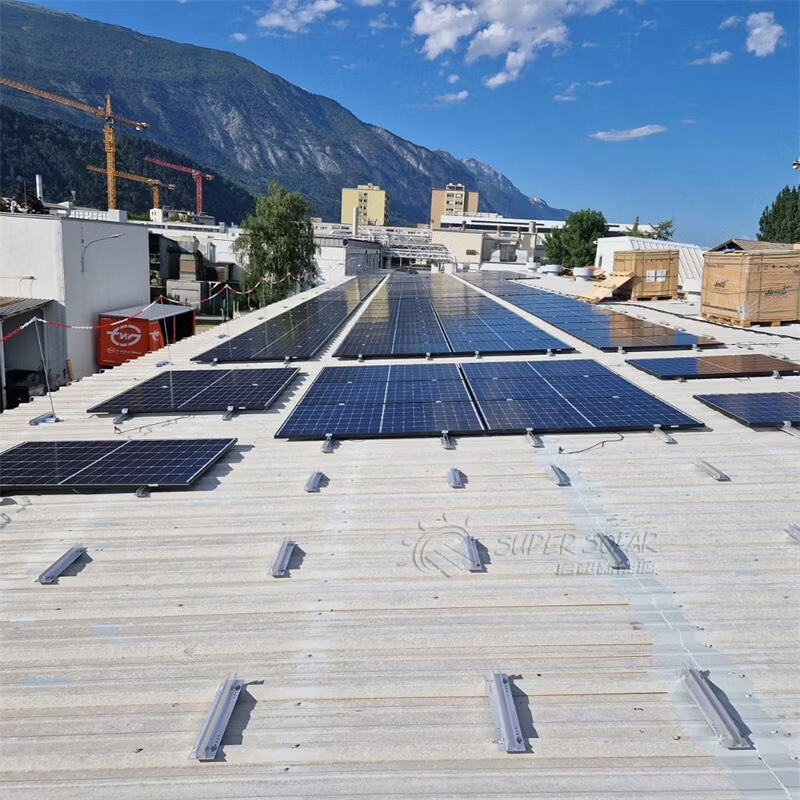

High wind areas are typically defined by local building codes rather than a single wind speed value.
Common examples include:
Coastal regions
Open terrain (low roughness)
Industrial buildings with large roof spans
Locations governed by standards such as EN 1991-1-4 or ASCE 7
Project wind zones (corner, edge, and field areas) must always be considered.
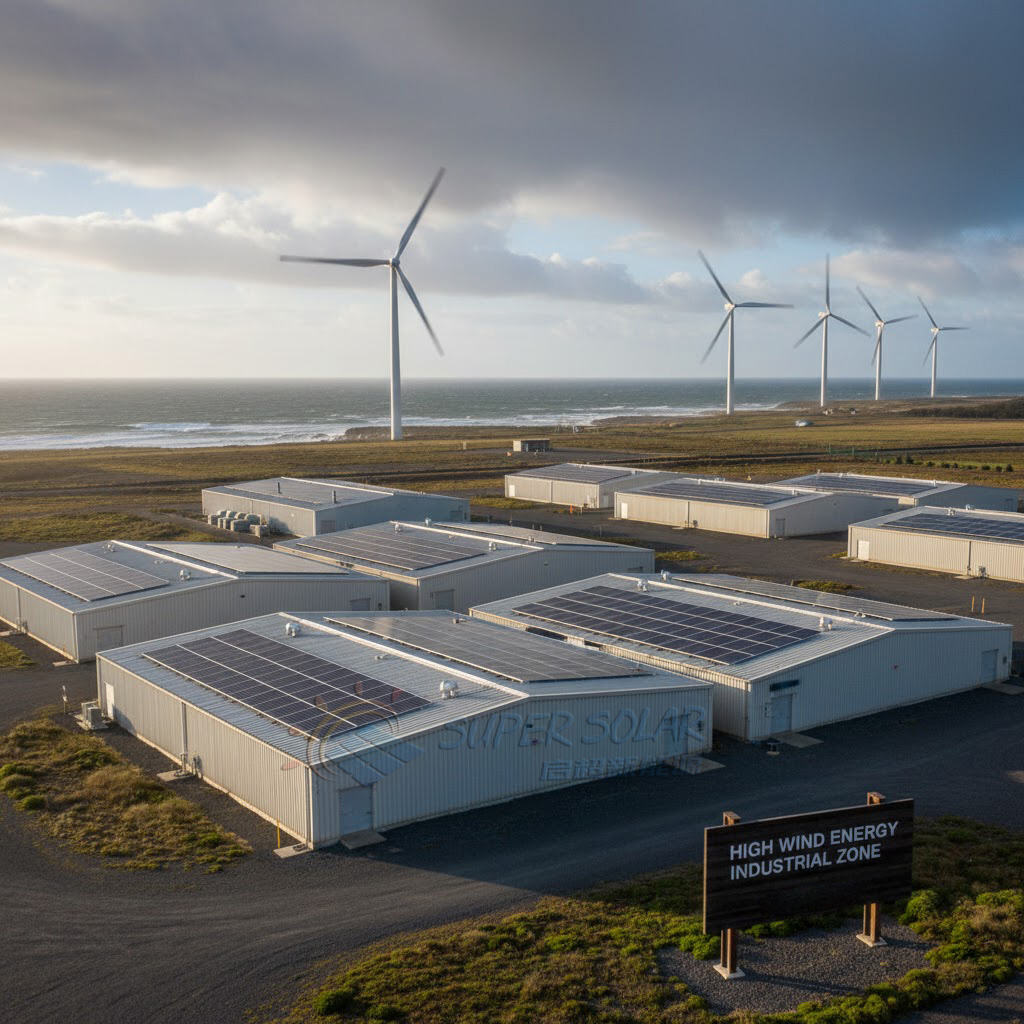

Because solar mini rails transfer loads directly to the roof sheet and purlins, roof condition is critical.
Minimum checks include:
Metal sheet thickness and material grade
Purlin spacing and fastening method
Roof age and corrosion condition
Existing roof load documentation, if available
Mini rails should not be used on thin, aged, or undocumented roof sheets in high wind zones.
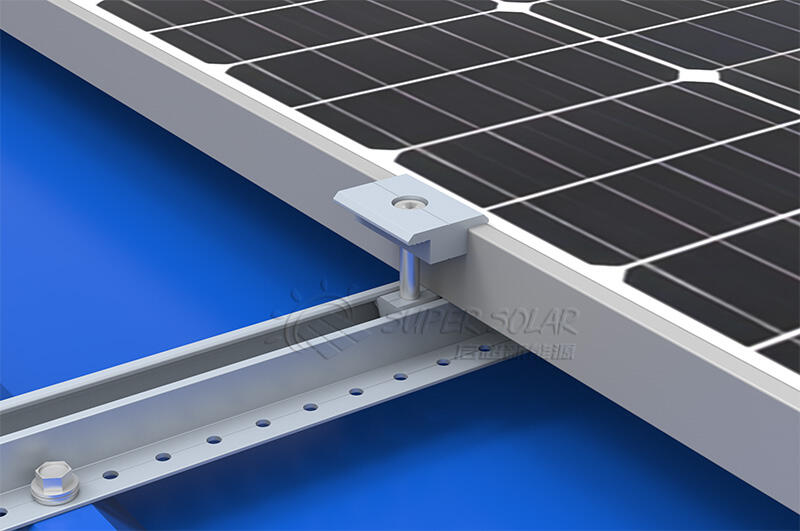

Fasteners are the primary load-bearing components in mini rail systems.
Best practices:
Use certified stainless steel self-drilling screws
Verify pull-out and pull-over resistance through testing or engineering data
Increase fastener quantity per mini rail if required by calculations
Apply controlled installation torque
Fastener failure is the most common risk factor in high wind mini rail projects.
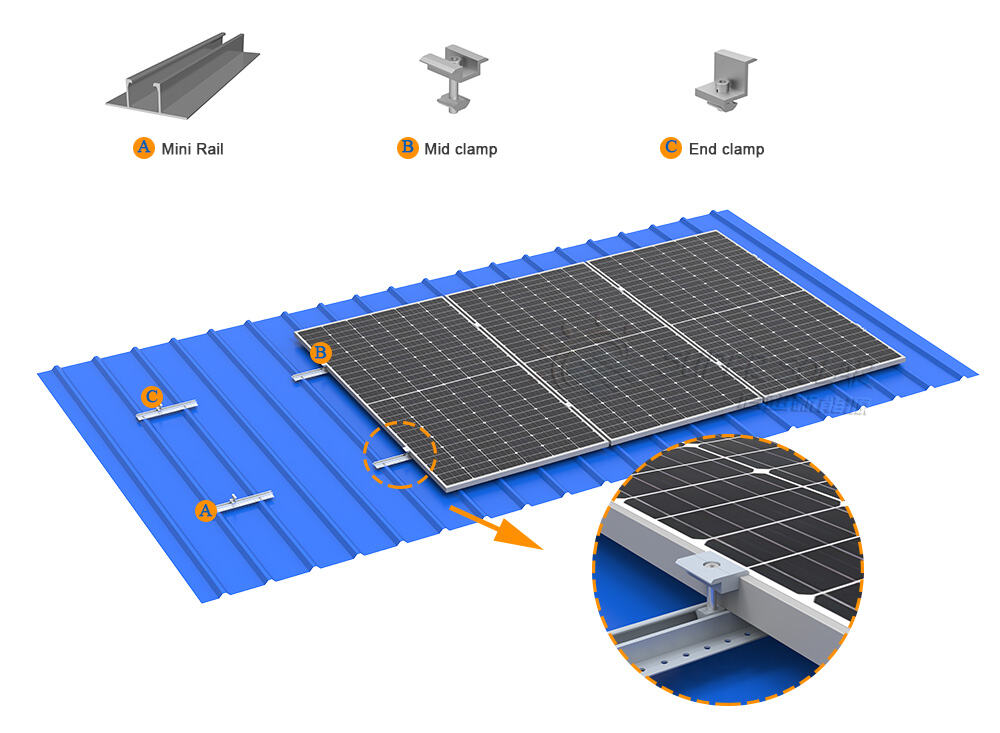
In high wind areas, default spacing values should never be used.
Engineering calculations should define:
Maximum allowable rail spacing
Required fastener quantity per rail
Additional fixing in roof edge and corner zones
Mini rail spacing is often significantly reduced compared to standard wind regions.
High wind projects require stricter installation control:
Use torque-controlled tools
Inspect EPDM sealing washers for proper compression
Conduct visual checks after installation
Perform random pull-out tests where required
Installation quality has a direct impact on long-term system performance.

| Evaluation Factor | Solar Mini Rail | Full Rail System |
|---|---|---|
| Material efficiency | High | Moderate |
| Structural redundancy | Lower | Higher |
| Engineering flexibility | Limited | High |
| Installation tolerance | Lower | Higher |
| Recommended risk level | Low–medium (engineered) | Medium–high |
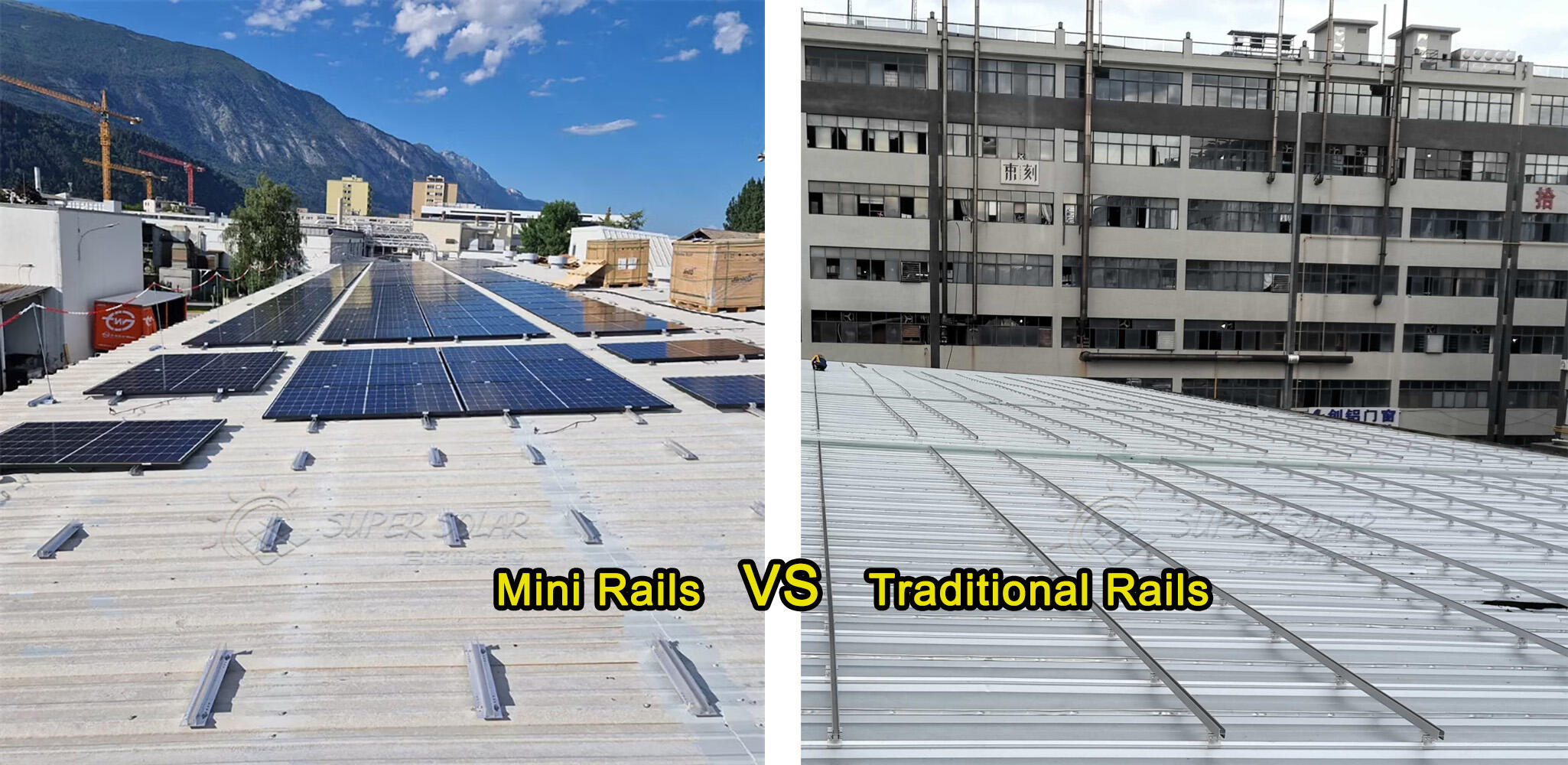
For projects with uncertain roof conditions or extreme wind exposure, full rail systems are generally preferred.

Before approving a solar mini rail system, confirm:
Structural calculations are available
Roof sheet and fastener data are verified
Rail spacing is adjusted for wind zones
Installation team has relevant experience
If any item cannot be confirmed, reconsider system selection.

Solar mini rail systems can be used in high wind areas, but they are not a default solution. Successful application depends on engineering verification, conservative design, and strict installation control.
For projects with high uncertainty or extreme exposure, a full rail system provides a higher safety margin and lower long-term risk.
Every project is unique. Contact our structural engineers to ensure your PV system is optimized for local wind and snow loads.
 Hot News
Hot News2025-11-03
2025-10-22
2025-01-24
2024-06-12
2024-06-12