Solar Mounting Systems
Contact Us
- Building A06, Jimei Software Park, Xiamen, China
- +86-592-6683155
- [email protected]
This guide helps EPC contractors, installers, and distributors determine whether a solar mini rail system is suitable for their specific project, and how to select the correct configuration to reduce installation risk and long-term issues.
Unlike marketing brochures, this selection guide focuses on engineering logic, roof conditions, and project constraints.
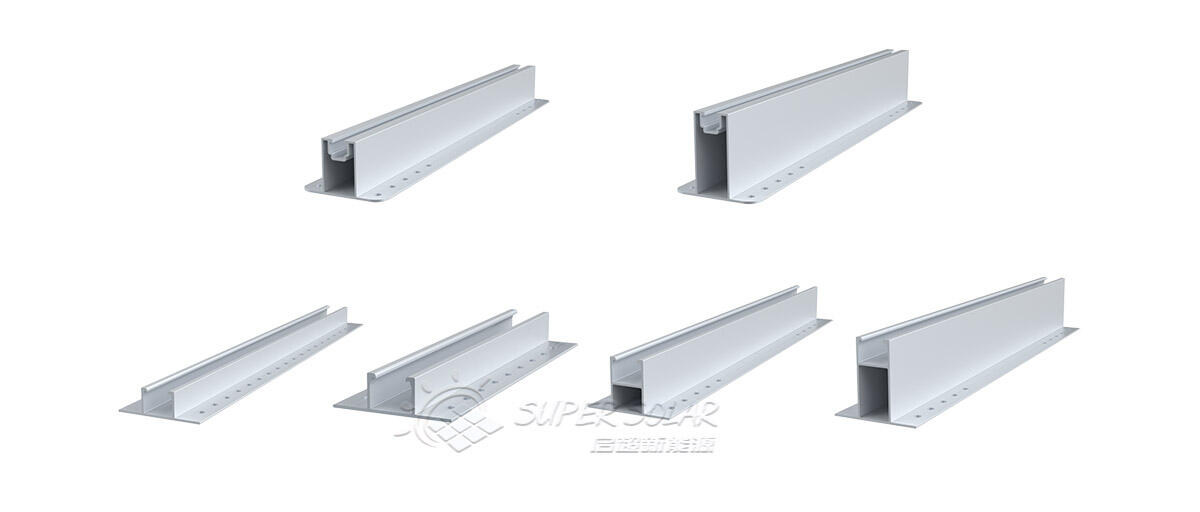

A solar mini rail mounting system is most suitable when all or most of the following conditions are met:
· The roof is a trapezoidal or corrugated metal sheet roof
· Roof sheet thickness and purlin spacing are known and verified
· The project prioritizes fast installation and cost efficiency
· Environmental loads are moderate or properly engineered
· The roof layout is simple and consistent
If these conditions are not met, a full rail system may provide a higher safety margin.
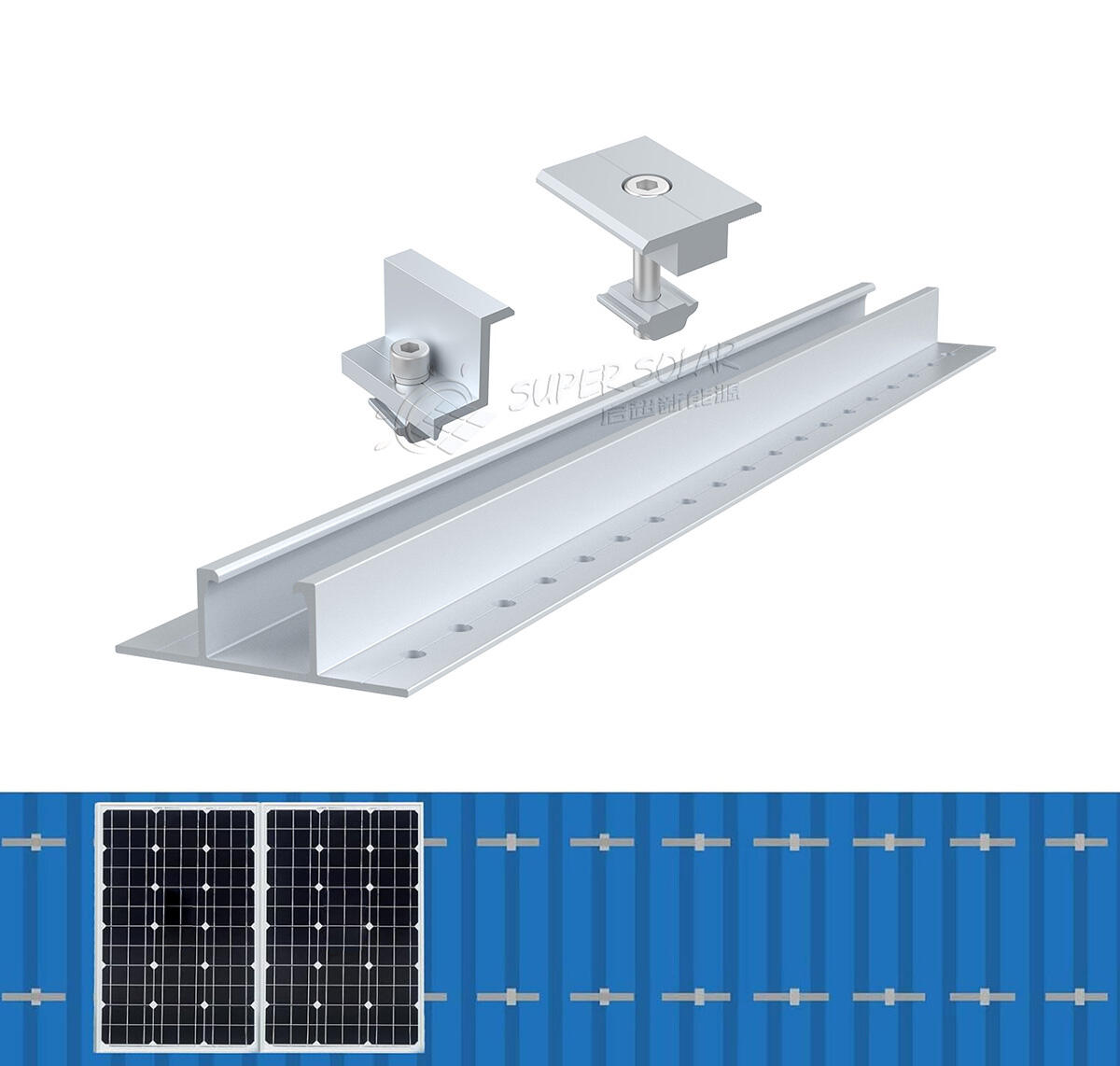

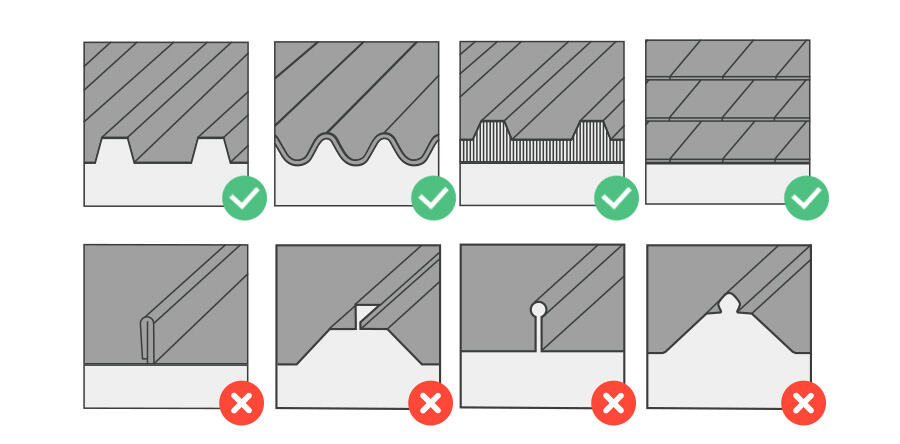
Before selecting a mini rail system, evaluate the roof type carefully.
· Trapezoidal metal sheet roofs
· Corrugated metal roofs
· Standing seam metal roofs (non-penetrating clamps required)
· Thin or aged metal sheets with unknown load performance
· Roofs with irregular purlin spacing
Solar mini rails can be used in a wide range of environments if load calculations are applied correctly.
Key factors include:
· Local wind speed and terrain category
· Snow load requirements
· Building height and roof zones
For high wind or snow load areas, mini rail spacing and fastener quantity must be adjusted based on structural calculations.
Because mini rail systems transfer more load directly to the roof sheet, fastener selection is critical.
Checklist:
· Use certified stainless steel self-drilling screws
· Verify pull-out and pull-over strength
· Apply correct installation torque
· Ensure EPDM sealing washers are properly compressed
Fastener failure is one of the most common causes of mini rail system issues.
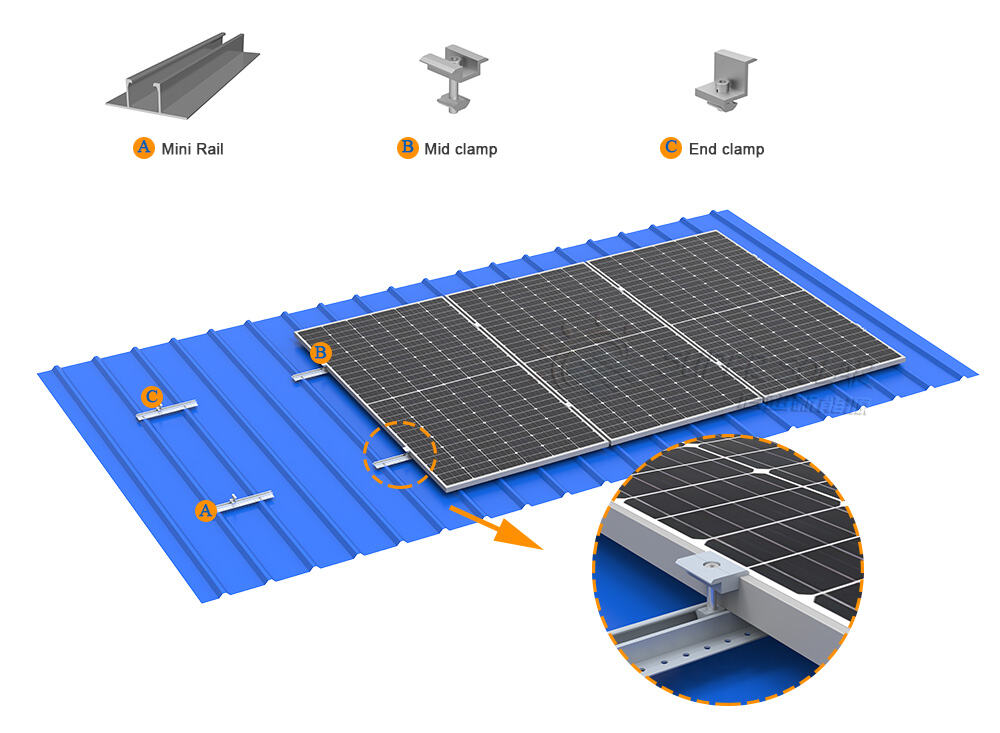
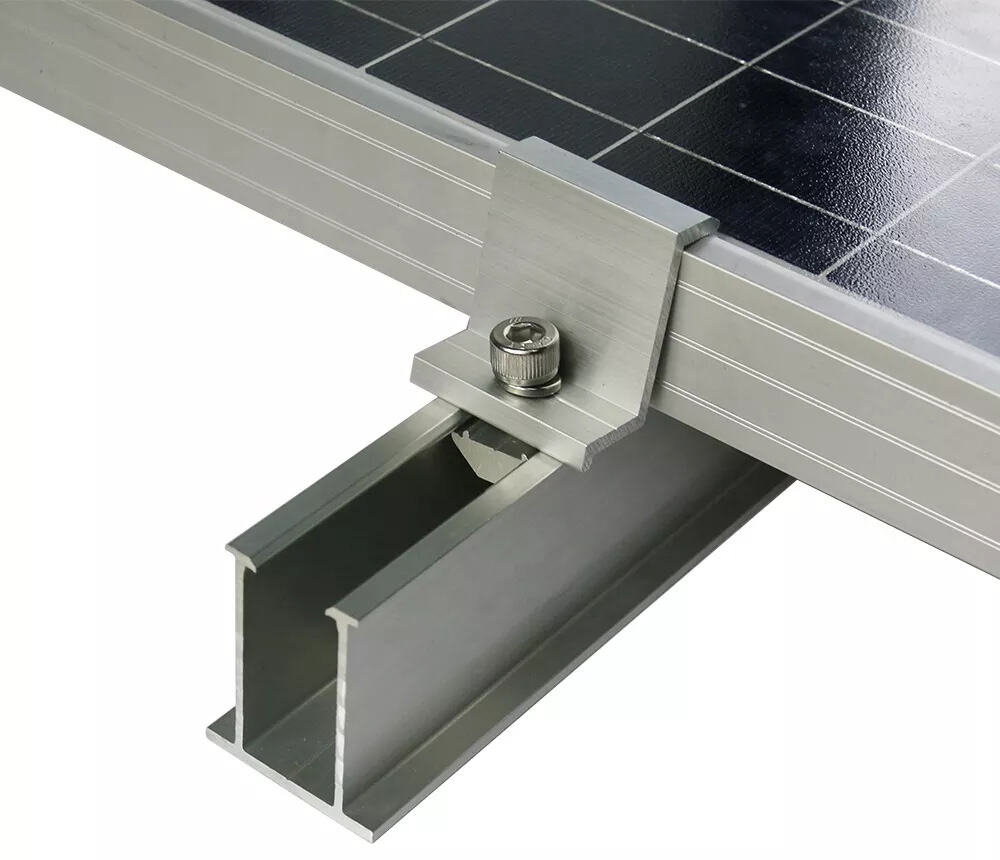
Before finalizing the system, confirm module compatibility:
· Module frame thickness (commonly 30–40 mm)
· Clamp type and grounding method
· Module manufacturer installation guidelines
Mini rails are compatible with most framed modules, but tolerances are smaller than full rail systems.
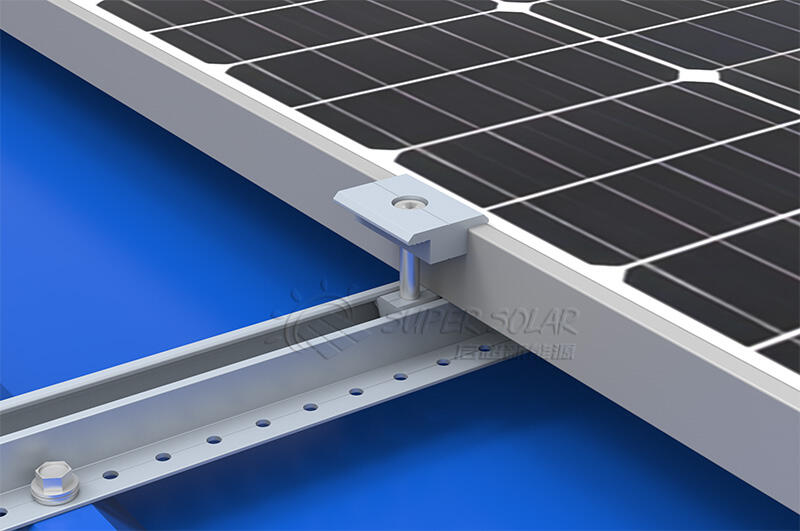

Recommended installation practices:
· Pre-mark rail positions according to engineering layout
· Use torque-controlled tools
· Perform visual inspection of seals and fasteners
· Conduct random pull-out tests if required by the project
Good installation practice is essential for long-term reliability.
· Selecting mini rails without checking roof sheet strength
· Using generic screws without load verification
· Over-tightening or under-tightening fasteners
· Ignoring local wind or snow load standards
Avoiding these mistakes significantly reduces project risk.
| Condition | Recommended System |
|---|---|
| Simple metal roof, cost-driven | Solar Mini Rail |
| High wind or snow load | Full Rail (preferred) |
| Complex roof geometry | Full Rail |
| Fast installation priority | Solar Mini Rail |
| Maximum structural redundancy | Full Rail |
solar mini rail vs full rail comparison
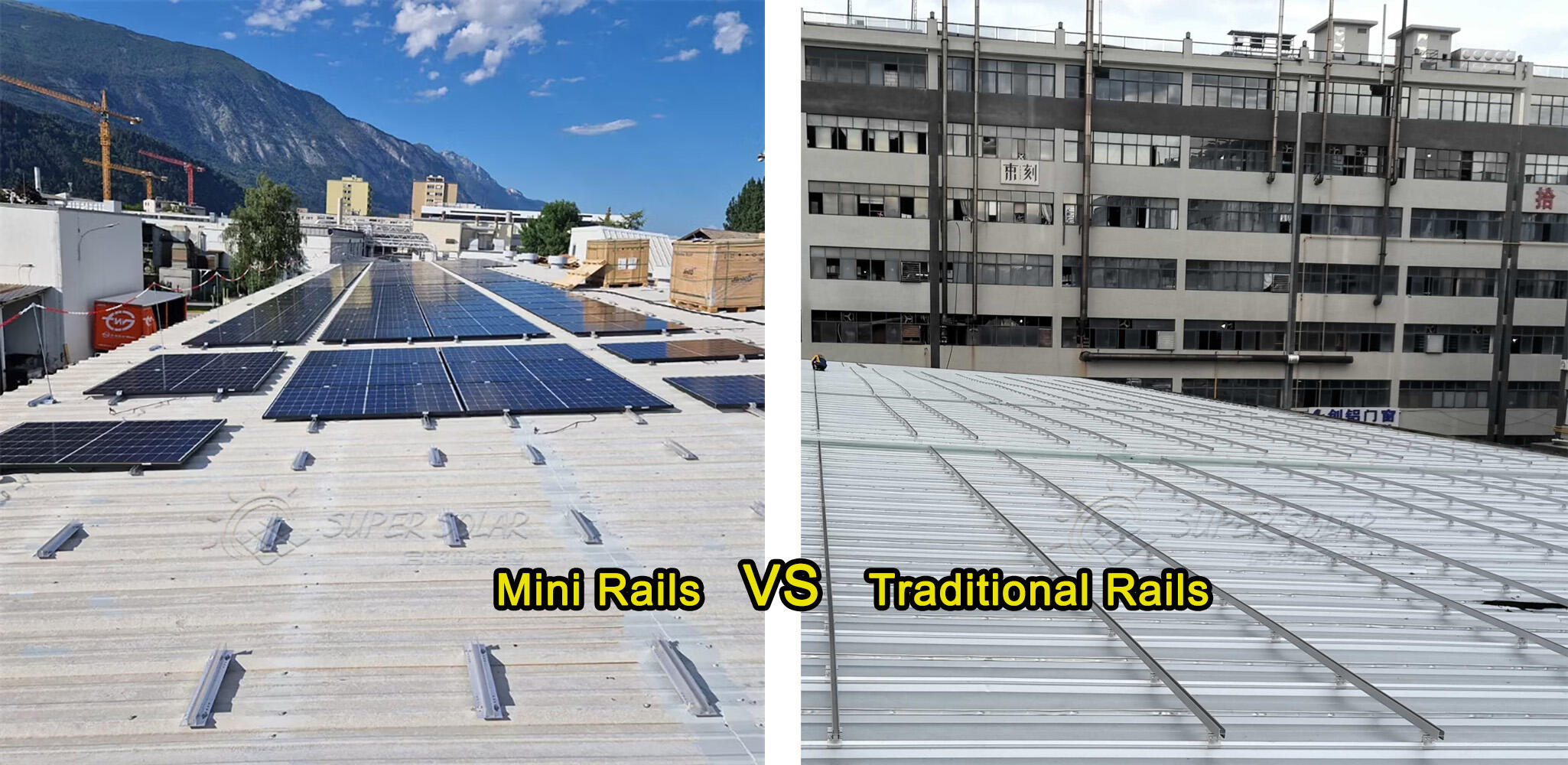

A solar mini rail system is not a "one-size-fits-all" solution. When applied to the right roof type and project conditions, it offers excellent cost efficiency and installation speed. When conditions are uncertain or extreme, full rail systems provide a higher safety margin.
Using a structured selection process helps EPC contractors and installers make informed decisions and avoid long-term performance risks.

 Hot News
Hot News2025-11-03
2025-10-22
2025-01-24
2024-06-12
2024-06-12